Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Cisco has disclosed a critical zero-day vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-20352, affecting all supported versions of Cisco IOS and IOS XE. The flaw, already being actively exploited in the wild, impacts as many as 2 million exposed devices worldwide. It originates from a stack overflow bug in the SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) component, which is responsible for handling network management data. The vulnerability carries a CVSS severity score of 7.7, enabling attackers to launch denial-of-service (DoS) attacks or, in certain cases, achieve remote code execution (RCE) with root privileges. Cisco confirmed that exploitation was observed after attackers compromised local administrator credentials.
To exploit the flaw for RCE, an attacker must have access to a device’s SNMP read-only community string or valid SNMPv3 credentials. These strings are often shipped with default values, remain widely known within organizations, and sometimes are left unchanged, making them a prime target. Once exploited, attackers can escalate privileges to root, bypassing even administrative restrictions. Security researcher emphasized that achieving root-level access on Cisco devices represents a particularly severe breach, as such privileges surpass what administrators are supposed to hold.
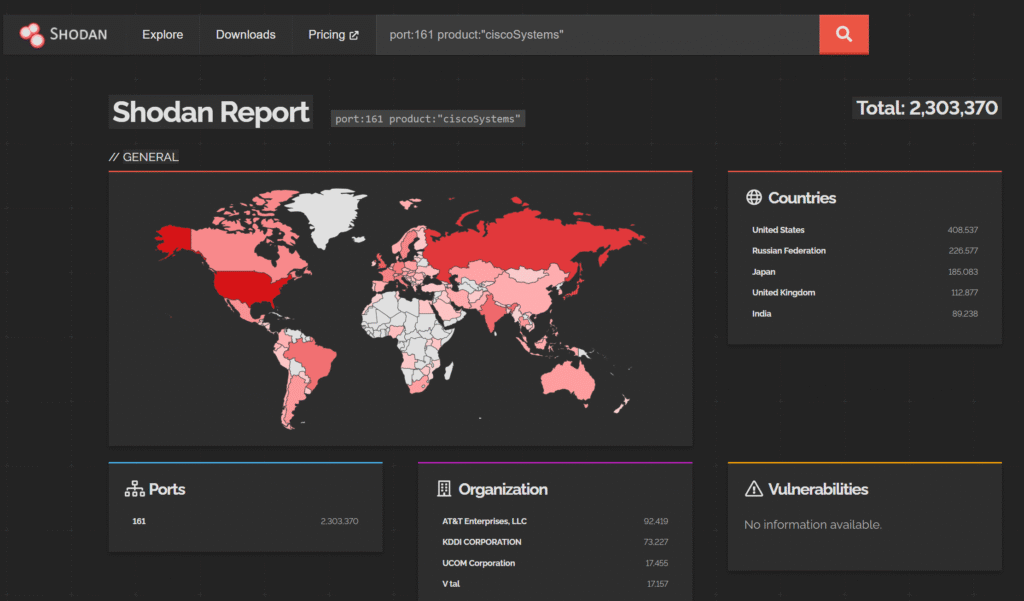
For denial-of-service attacks, the requirements are less stringent: an attacker only needs valid SNMP credentials to crash vulnerable devices remotely. This risk is compounded by the poor security practice of exposing SNMP services directly to the Internet. Shodan scans confirm that more than 2 million Cisco devices have SNMP exposed, highlighting a massive attack surface for opportunistic and targeted campaigns alike. As a result, organizations that fail to properly restrict or monitor SNMP exposure face an elevated likelihood of compromise.
Cisco has already released fixed software updates to address the issue, urging customers to upgrade immediately. For organizations unable to patch right away, the company recommends restricting SNMP access strictly to trusted users and monitoring devices using SNMP commands to detect anomalies. However, Cisco made it clear that there are no workarounds available, reinforcing that patching is the most effective defense. This zero-day is part of Cisco’s September update, which included 14 patched vulnerabilities, eight of which carried high-severity ratings between 6.7 and 8.8. The scale of exposure and active exploitation underscores the urgency for administrators to act swiftly to mitigate risks.
Impact
- Code Execution
- Privilege Escalation
- Denial of service
Indicators of Compromise
CVE
- CVE-2025-20352
Remediation
- Upgrade immediately to the fixed versions of Cisco IOS and IOS XE released by Cisco.
- Restrict SNMP access so only trusted users and secure internal networks can query devices.
- Block SNMP exposure to the Internet, ensuring SNMP is only accessible through secured management networks.
- Replace or randomize default SNMP community strings, avoiding commonly known or weak credentials.
- Enforce SNMPv3 with strong authentication and encryption instead of using insecure SNMPv1/v2c.
- Monitor SNMP activity using the snmp command and logging tools to detect suspicious or unauthorized access attempts.
- Review and rotate local administrator credentials to reduce the chance of attackers leveraging stolen accounts.
- Harden device configurations by disabling unnecessary services and applying Cisco’s security best practices.

