Severity
High
Analysis Summary
The Muhstik botnet known for targeting IoT devices and Linux servers has been exploiting a critical security flaw (CVE-2023-33246) in Apache RocketMQ to expand its reach. This flaw, which has a CVSS score of 9.8, allows remote and unauthenticated attackers to execute code on vulnerable servers by forging RocketMQ protocol content or using the update configuration function.
Once the vulnerability is exploited, the attackers execute a shell script from a remote IP which then downloads the Muhstik malware binary ("pty3"). This malware achieves persistence by copying itself to multiple directories and modifying the /etc/inittab file to restart during boot effectively evading detection by masquerading as a pseudoterminal and running directly from memory.
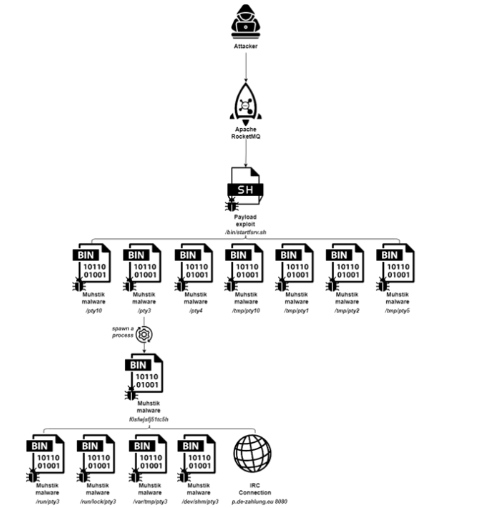
Researchers said in a report that Muhstik first documented in 2018 is notorious for leveraging known vulnerabilities in web applications to propagate. It not only performs cryptocurrency mining but also launches DDoS attacks. After infecting a system, the malware gathers system metadata, moves laterally to other devices via SSH, and communicates with a command-and-control domain using IRC.
The malware's ultimate goal is to conduct various flooding attacks overwhelming target network resources and causing denial-of-service conditions. Despite the public disclosure of the RocketMQ flaw over a year ago, more than 5,200 instances remain vulnerable, highlighting the need for organizations to update to the latest version.
The persistence of vulnerabilities like CVE-2023-33246 poses significant risks as attackers can continue to exploit unpatched systems. Muhstik's ability to spread through these flaws and execute cryptocurrency mining emphasizes the dual objectives of spreading infection and generating illicit gains. This ongoing threat underscores the importance of timely patching and robust security measures to protect systems from such exploits. Security researchers stress the critical need for vigilance and proactive defense against these persistent threats.
In addition to the RocketMQ vulnerability, poorly secured MS-SQL servers are also being targeted by various malware types, including ransomware and remote access trojans. To safeguard against these attacks, administrators are advised to use strong, frequently-changed passwords and apply the latest security patches. These preventive measures are crucial in mitigating brute-force and dictionary attacks as well as vulnerability exploits to protect database servers and maintain robust cybersecurity defenses.
Impact
- Denial of Service
- Cryptocurrency Theft
- Information Theft
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- p.de-zahlung.eu
- p.deutschland-zahlung.eu
IP
- 91.148.224.34
- 89.36.76.42
- 89.36.76.38
- 51.79.19.53
- 194.59.165.52
- 138.197.78.18
- 91.200.43.22
- 139.180.185.248
- 161.35.219.184
MD5
- 7822cdf1cf8e30d9997c9743f8897f33
- 725fbb0b0f56ed37c19575e2aa944207
- e5cb7c6e69bcfee5c42e4c288669482c
- 7a7e204b54f1a5da1493b960b1a31a3a
- 2052ec4a3d8a89a121ac0efa68f11509
- f895104d7e20dc6808c05164103d1357
SHA-256
- 9e28f942262805b5fb59f46568fed53fd4b7dbf6faf666bedaf6ff22dd416572
- 1f9cda58cea6c8dd07879df3e985499b18523747482e8f7acd6b4b3a82116957
- 176c57e3fa7da2fb2afcd18242b79e5881c2244f5ab836897d4846885f1bd993
- a7bf3c031ab66265ce724fc26c8f7565442a098b06b01ea8871f13179d168713
- 6730eb04edf45d590939d7ba36ca0d4f1d2f28a2692151e3c631e9f2d3612893
- 86947b00a3d61b82b6f752876404953ff3c39952f2b261988baf63fbbbd6d6ae
SHA1
- 0f97481dd038a7a894d31f49148a6d03ddc66921
- e4ed085f360d920f8fc15e3496a6e8ea9e1f1f2c
- 9f6b0a9fd9a5983c1e53254cd4ab7a2584fd168c
- 4f727feebbd65107b80427c60439372a9896661e
- 2200245b6571d74c9ddc476fa3fa218d1a68f335
- aec367a2ac984b1695edeab3717c663212487b6f
Remediation
- Upgrade to the latest version of Apache RocketMQ, available from the Apache Website.
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Perform comprehensive security audits on the email server infrastructure to identify and address any potential weaknesses. This includes reviewing server configurations, access controls, and encryption protocols to ensure they meet industry best practices.
- Emails from unknown senders should always be treated with caution. Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.
- Enable 2FA for user accounts on the email server to add an extra layer of security. This prevents unauthorized access even if usernames and passwords are compromised.
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Implement network segmentation to isolate critical systems and sensitive data from the rest of the network. This limits the lateral movement of attackers in case of a breach and reduces the impact of potential future attacks.
- Implement a regular backup strategy for email servers and critical data. Ensure that backups are stored securely and regularly tested for data restoration.
- Apply the latest security patches and updates to the email server software and associated components to address any vulnerabilities that may have been exploited. Also, prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities and zero-days.

