Severity
High
Analysis Summary
The EMERALDWHALE campaign is a large-scale operation targeting exposed Git configuration files to collect sensitive credentials, clone private repositories, and extract cloud credentials from source code.
According to the report, this threat has accumulated data from over 10,000 private repositories, storing these stolen credentials in an Amazon S3 bucket, which Amazon has since shut down. The stolen data includes credentials for Cloud Service Providers (CSPs), email providers, and other services, primarily used for phishing and spam campaigns.
EMERALDWHALE's operation, though not highly sophisticated, utilizes a range of tools to exploit exposed Git configurations, Laravel .env files, and other web data. The threat actors behind this campaign scan a wide range of IP addresses to locate vulnerable servers and Git repositories, extracting credentials embedded in these files. By leveraging these credentials, the group can clone both public and private repositories obtaining additional sensitive information which is then uploaded to the S3 bucket.
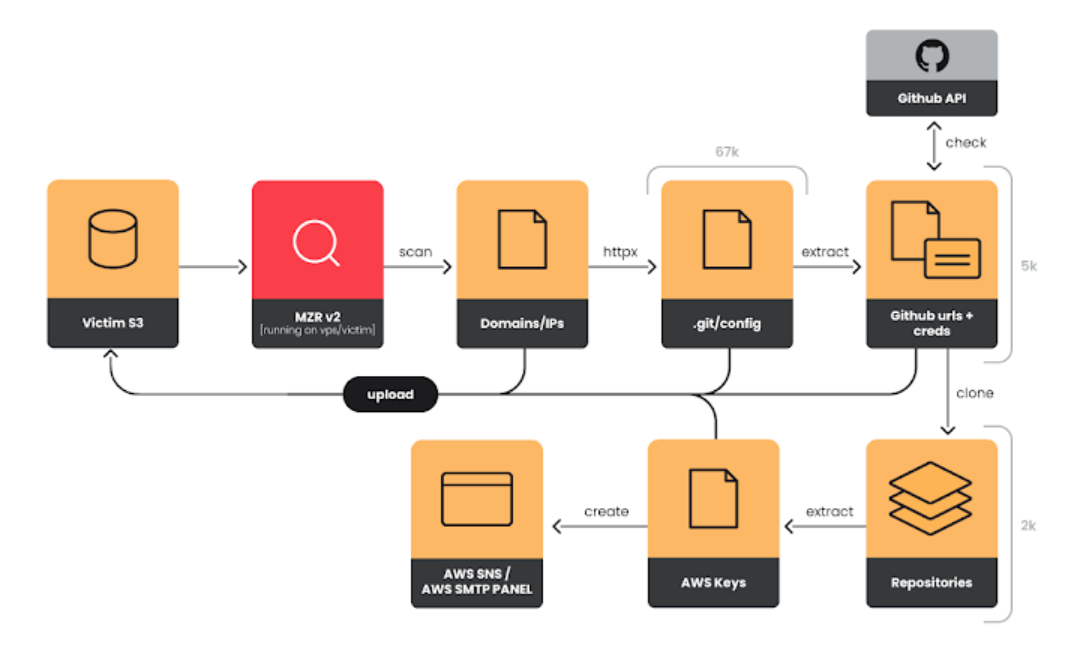
The toolset used by EMERALDWHALE includes MZR V2 and Seyzo-v2 both sold on underground forums and equipped to scan and exploit exposed Git repositories. These tools take IP address lists generated from search engines like Google Dorks and Shodan and use utilities like MASSCAN to locate and access misconfigured repositories. This enables them to easily search for relevant configuration files, providing an efficient path to extract and validate credentials.
The analysis revealed that over 67,000 URLs with the path "/.git/config" are exposed and sold for $100 on Telegram, indicating a growing market for Git and other configuration files containing sensitive information. In addition to Git files, the attackers target Laravel .env files, which often contain critical credentials for cloud providers and databases. This attack underscores the risks associated with poor secret management practices, as exposed credentials can significantly compromise cloud and web services.
Impact
- Credential Theft
- Unauthorized Access
- Exposure of Sensitive Data
Remediation
- Ensure all Git repositories, especially configuration files, are private and require authentication.
- Disable public access to configuration and environment files by restricting permissions to trusted users and IPs.
- Avoid storing sensitive credentials directly in the source code. Instead, use a secure secret management solution.
- Rotate keys and credentials regularly and immediately replace any compromised credentials.
- Regularly scan for exposed files, like .git/config and .env, using tools that detect exposed files or sensitive data.
- Utilize vulnerability scanners and tools like Shodan and Google Dorks to identify exposed assets proactively.
- Limit access to cloud storage services by configuring firewalls and access control policies.
- Regularly review and update permissions for S3 buckets or other cloud storage to avoid accidental exposure.
- Set up logging and monitoring for unusual access to repositories and cloud services.
- Use intrusion detection systems (IDS) and set up alerts for suspicious access patterns, such as large downloads or unauthorized IP addresses.
- Train team members on the importance of secure coding and handling of configuration files.
- Encourage the use of environment variables for sensitive information rather than storing credentials in files directly.
- Enable MFA for all accounts accessing critical systems, repositories, and cloud services to add an extra layer of security.

