Severity
High
Analysis Summary
A new phishing campaign is targeting governments in the Middle East and is distributing an initial access downloader called IronWind. It was detected between July and October 2023, and researchers have attributed it to a threat actor tracked as TA402.
TA402 is a Middle Eastern advanced persistent threat (APT) group that has always proven to be a highly sophisticated group for cyber espionage that focuses on collecting intelligence. It constantly updates the IronWind malware’s delivery mechanisms, like using XLL file attachments, Dropbox links, and RAR archives.
Using IronWind is a big shift from TA402’s previous attack chains, which utilized the use of a backdoor dubbed as NimbleMamba that also targeted Middle Eastern governments and foreign policy think tanks.
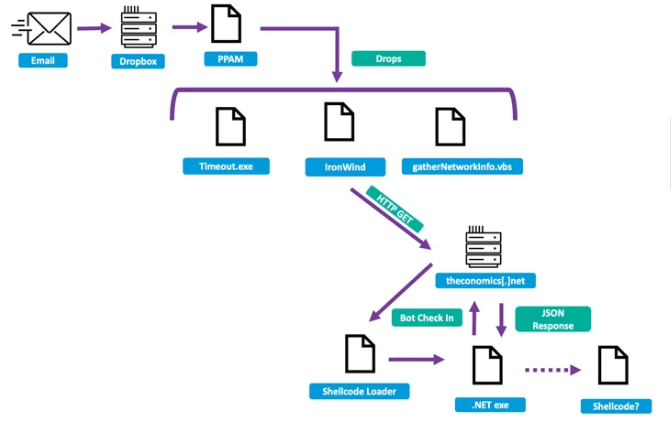
The latest campaign on this APT uses a stolen email account that belongs to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and sends out phishing lures using Dropbox links hosting the deployment of IronWind. The downloader then receives additional payloads from a C2 server, which includes a post-exploitation toolkit called SharpSploit.
In August and October of 2023, some social engineering campaigns were discovered to take advantage of XLL file and RAR archive attachments that were embedded in emails to deploy IronWind. The group is also known to use geofencing techniques that can make detection difficult.
TA402 continues to iterate and use new delivery methods to bypass detection from security software. They utilize complicated infection chains and new malwares to attack their targets.
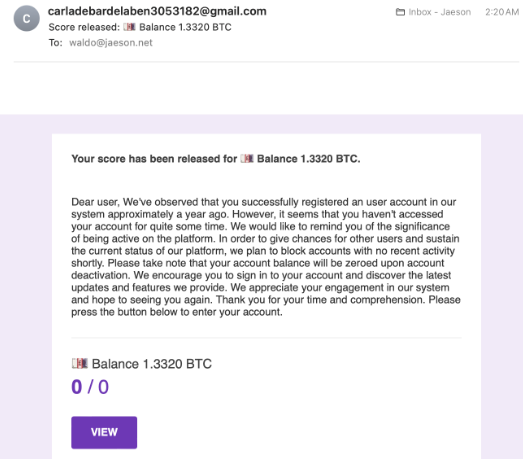
The development comes as researchers revealed that the threat actors have been exploiting the “Release scores” feature of Google Forms quizzes in order to deliver email and carry out cryptocurrency scams.
Cybersecurity researchers stated, “The emails originate from Google’s own servers and consequently may have an easier time bypassing anti-spam protections and finding the victim’s inbox.”
Impact
- Cyber Espionage
- Sensitive Data Theft
- Cryptocurrency Theft
- Financial Loss
Indicators of Compromise
IP
- 5.149.249.74
- 154.53.56.231
- 154.53.63.93
- 192.3.101.111
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls
- Do not download documents attached in emails from unknown sources and strictly refrain from enabling macros when the source isn’t reliable.
- Emphasize the importance of verifying the legitimacy of emails, even if they appear to come from trusted sources.
- Implement advanced email filtering solutions that can detect and block phishing emails before they reach users’ inboxes.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions in a timely manner. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets
- Along with network and system hardening, code hardening should be implemented within the organization so that their websites and software are secure. Use testing tools to detect any vulnerabilities in the deployed codes.
- Maintain daily backups of all computer networks and servers.
- Keep all software, operating systems, and applications up to date with the latest security patches.
- Continuously monitor network and system logs for unusual or suspicious activities.
- Deploy security information and event management (SIEM) solutions to centralize log analysis.
- Keep web browsers and browser extensions up to date to mitigate potential vulnerabilities that threat actors might exploit.
- Review and secure website code to prevent open redirect vulnerabilities.
- Implement robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) solutions
- Verify the legitimacy of both source and target URLs instead of assuming their safety, and consider using session isolation solutions to protect against real-time zero-hour phishing attacks.

