Severity
High
Analysis Summary
A new bot made of firewalls and routers from Cisco, Fortinet, NETGEAR, and DrayTek has been discovered being used as a covert data transfer network by various advanced persistent threat (APT) groups like the Chinese threat actor dubbed Volt Typhoon. The botnet is dubbed KV-botnet by researchers and is a combination of two activity clusters that were first discovered in February 2022.
The campaign can infect devices that are present at the edge of networks. The two clusters, named KV and JDY, are distinct but can work together to gain access to high-profile victims and establish a covert infrastructure. The data shows that the botnet is controlled from IP addresses from China.
The researchers said, “The “JDY cluster,” named for artifacts in the x.509 certificate, implemented less sophisticated techniques to perform targeting scanning; and the “KV cluster,” which appears to be reserved for manual operations against higher value targets selected by the JDY component.”
Security analysts suspect that Volt Typhoon is one of the users of the KV-botnet and it holds a subset of their operational infrastructures, shown by the large decline in their operations during June and early July 2023 after it was publicly disclosed that the adversary was targeting critical infrastructure in the U.S.
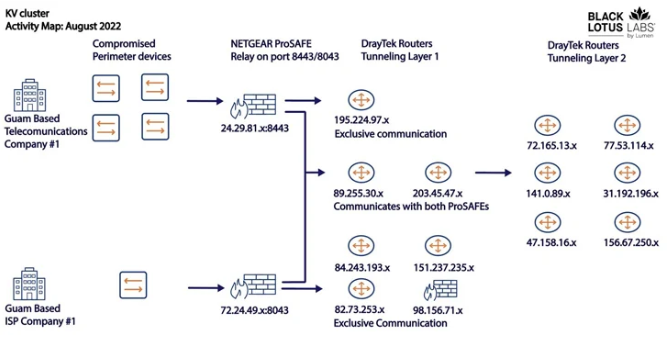
Microsoft was the first one to expose the threat group’s tactics and said that it tried to mix in with usual network activity by routing traffic using compromised small office and home office (SOHO) network devices, like routers, VPN hardware, and firewalls. The initial access vector used to infect devices is currently unknown, but it is followed up by the first-stage malware which is responsible for removing security software and any other malware strains to make sure only it remains present on the compromised devices. It can also retrieve the main payload from a remote C2 server as well as upload and download files, execute additional modules, and run commands.
Within the previous month, the botnet’s infrastructure has shown some upgrades by focusing its attacks on Axis IP cameras, which indicates that the threat actors could be preparing for a new wave of cyberattacks. One of the notable aspects of this campaign is that all the tools used completely reside inside the memory, making detection very challenging and allowing the attackers to achieve long-term persistence. Due to the malware residing in memory, the infection can be stopped by power-cycling the device, which removes the threat but re-infection is still highly likely to happen.
It was reported that about two dozen critical organizations, namely water, power, transportation, and communication sectors, in the U.S. were infiltrated by Volt Typhoon within the past year. The threat actors are known to hide their tracks by tunneling their attacks using innocuous machines like home or office routers before reaching their targeted users.
Impact
- Unauthorized Access
- Exposure to Sensitive Data
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- be956ab9fccf11e75b6d285bf8878fb6
- 2efacc5e91451d7de389f46e6acb9839
- f03b295c176dceefd9b801f2eafbeb50
- 0c8b4fb78d6ac5fa699bdb404829ece1
- 38d167722d181d4364b9f64fa9da0d6f
- 16bfb98d6a9093989bcd1faf8975a968
- af4558175b6d967508d407054edf6282
- f32f7a7530a9b477755d40b1fbb1897c
- b517d9e55275fdd5c422e06853330481
- 424818f3edfc471bb0b2d47987f8fcd9
SHA-256
- 48299c2c568ce5f0d4f801b4aee0a6109b68613d2948ce4948334bbd7adc49eb
- 0279435f8727cca99bee575d157187787174d39f6872c2067de23afc681fe586
- 2cb6df289475457e807fc202a2b4688b2e23a88c94a8431981780caf8b76acf7
- b4f2470159ca93f9d585ae2df1da972f6d14a0c418ebc202a324b9be5c877b61
- d6cd1636569bba4131462bb8f45be1daa9a203aa343b6f2fd48a4847acfc29fa
- 3fab16ec4643d8f6b9a99d85427322f7fb40e9ea3cd4de8318c6a52e29869d5a
- 86f01d5342ec39c65b1cff716f19c334cec26a82b87492d783d5e8f4ff9cb63a
- 19aa5a2235ee2518826a48363cb603060ee73ddccdf7d93bf197f97d7402aa37
- c524e118b1e263fccac6e94365b3a0b148a53ea96df21c8377ccd8ec3d6a0874
- 2711f1341d2f150a0c3e2d596939805d66ba7c6403346513d1fc826324f63c87
SHA-1
- f45f6af053f083d12407039ef9418a0f450a768e
- 6646fd47984c0ced92890af32d6e0b1b7985e6b4
- 8345e45bcb3db6b336d901ebabfed01f38d4d8ce
- 28bddb8d9c581db86ef038be09fb82d96829dfb8
- ada79334e1f52efb61441fd19735f5c71dbd978b
- 525e53f1f87e7ebe36b28db9c8d827af0b322bd8
- 48d6e05d889e38c856b1def4aed10c7e0bc9b753
- 35f33ac11b53b813b24386281440bd7354f11581
- 067f238d9d5c219d3c359dc398f5416f1a99c70b
- 08ad4f940d488587697820d13c3d175a05e5fa6c
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions on time. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets
- Immediately change default passwords on IoT devices to unique ones.
- Keep devices’ firmware and software up to date to ensure that known vulnerabilities are patched.
- Isolate IoT devices from critical systems by segmenting your network.
- Implement firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor and control traffic to and from IoT devices.
- Employ tools that can identify unusual behavior or traffic patterns that might indicate a DDoS attack or a compromised device.
- Disable any unnecessary services or features on IoT devices to reduce their attack surface.
- Follow security best practices, such as disabling remote management if not needed and enabling security features provided by the device manufacturer.
- Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor for anomalous or malicious network activity.
- Set up alerts for unusual traffic patterns that might indicate a DDoS attack or a compromised device.

