Severity
High
Analysis Summary
A recent discovery highlights a year-long software supply chain attack targeting the npm package registry, exploiting trust in open-source dependencies. The malicious package, @0xengine/xmlrpc, initially presented itself as a legitimate JavaScript-based XML-RPC server and client for Node.js when it was uploaded on October 2, 2023. However, the next day, its version 1.3.4 introduced harmful code to steal sensitive data such as SSH keys, bash history, system metadata and environment variables. The stolen data was exfiltrated every 12 hours via Dropbox and file.io services with the package achieving 1,790 downloads to date.
According to the researchers, the attack employed two distribution methods. The first involved direct installation from npm. The second, more insidious method, integrated the malicious package as a dependency in a GitHub project repository named yawpp (Yet Another WordPress Poster). This tool, designed to automate WordPress posts, listed the latest version of @0xengine/xmlrpc in its "package.json" file, causing the malware to be automatically downloaded when users set up the yawpp tool. This approach leveraged the trust users place in dependencies though it remains unclear if the tool’s developer intentionally included the malicious package. The yawpp repository has since been removed from GitHub.
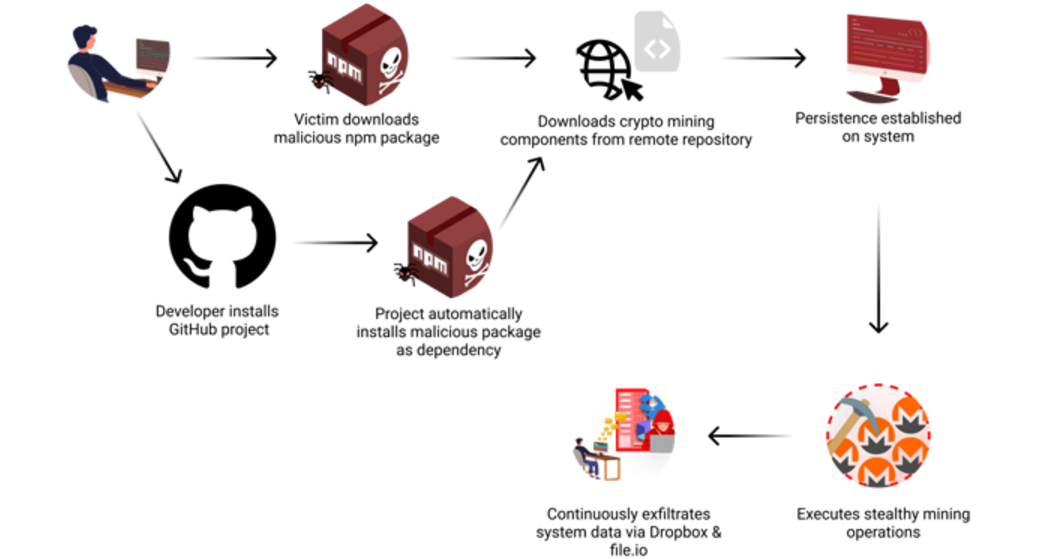
Once installed, the malware collected system data maintained persistence via system and deployed the XMRig cryptocurrency miner. The attacker’s Monero wallet revealed that 68 systems were actively compromised to mine cryptocurrency. Advanced evasive capabilities included monitoring for processes such as top, vmstat, and others, suspending mining operations if user activity was detected and terminating mining-related processes if administrative tools were running. These measures allowed the malware to remain stealthy and avoid detection.
This incident underscores the need for ongoing vigilance in the software supply chain. Researchers emphasized that even packages with longstanding maintenance histories can turn malicious through updates. This calls for rigorous vetting not just during initial installation but throughout a package’s lifecycle. Trust in open-source repositories must be accompanied by proactive security measures to detect and mitigate threats like these.
In related developments, Datadog Security Labs disclosed another malicious campaign involving fake npm and PyPI packages aimed at distributing stealer malware such as Blank-Grabber and Skuld Stealer. This campaign, tracked as MUT-8694, primarily targets Roblox developers using typosquatting techniques to mimic legitimate packages. The persistent efforts of these threat actors highlight the ongoing risk to open-source ecosystems, further emphasizing the importance of robust supply chain security practices.
Impact
- Sensitive Data Theft
- Crypto Theft
- Financial Loss
Remediation
- Regularly review dependencies and sub-dependencies for suspicious updates or unverified publishers.
- Use tools like npm audit, Dependabot, or Snyk to identify vulnerabilities in your packages.
- Avoid installing packages directly from registries without verifying their origin and reputation.
- Cross-check package versions and their recent changes before installation.
- Track updates to critical dependencies for unexpected or undocumented functionality.
- Utilize tools that can flag major changes in package behavior, such as diff tools or automated monitoring solutions.
- Use runtime security tools to detect unusual behavior, such as unauthorized data access or cryptocurrency mining.
- Monitor processes and system activity to identify anomalies, like high CPU usage or frequent data exfiltration attempts.
- Verify the integrity of repositories before cloning or using them, especially if they include dependencies.
- Avoid using repositories from untrusted or unknown developers.
- Limit the permissions granted to packages, restricting access to sensitive files, environment variables, or SSH keys.
- Containerize applications to isolate dependencies from critical system components.
- Educate developers about supply chain risks and best practices for dependency management.
- Train teams to recognize typosquatting and malicious package names.
- Encourage or require the use of digitally signed packages to ensure authenticity.
- Verify the signatures of packages before installation.
- Deploy static and dynamic analysis tools to scan dependencies for malware.
- Use tools like Socket, Checkmarx, or custom scripts to assess package behavior.
- Have a response strategy in place to quickly address supply chain attacks.
- Include procedures for removing malicious packages, revoking compromised keys, and restoring systems from backups.
- Report suspicious packages to npm, PyPI, or other registry maintainers to facilitate swift removal.
- Support efforts to improve security in open-source communities, such as creating stricter guidelines for package publishing

