Severity
High
Analysis Summary
A sophisticated cyberattack that targets users of Notepad++, a well-known text and code editor, has been discovered by researchers. A default plugin in the Notepad++ package has been effectively modified by threat actors, possibly jeopardizing the security of several systems.
The aforementioned plugin, "mimeTools.dll," is a built-in feature of Notepad++ that offers encoding features like Base64. When Notepad++ is run, it is immediately included and loaded, a feature that the attackers have taken advantage of. They were able to pass off the malicious code as an authentic component of the Notepad++ package by modifying the mimeTools.dll file.
This kind of attack, called DLL Hijacking, uses the plugin's automated loading to run malicious code embedded in it without the user's awareness. When the Notepad++.exe file is opened, the compromised mimeTools.dll loads, and the hidden malware is activated. Within mimeTools.dll, the attackers have inserted malicious shell code that is encrypted, along with the decryption and execution code.
After a thorough analysis by cybersecurity researchers, it was discovered that the malicious shell code was contained in the "certificate.pem" file inside the modified package. All of the plugin's original features are still operational despite the infection; the only code that has changed is the DllEntryPoint. This indicates that whether or not the user tries to use any particular plugin feature, the malicious activity starts as soon as the DLL loads.
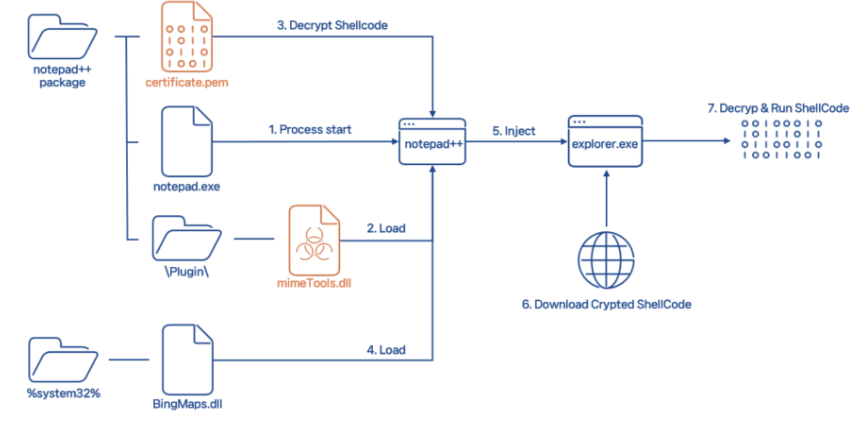
Running Notepad++ loads the malicious mimeTools.dll, which decrypts and runs the shell code from the certificate.pem file. This is the malware's execution flow. Later on in the attack, communication with a command and control (C2) server makes it easier to decrypt more code and run more shell scripts. It has now been discovered that the C2 server displays a WordPress login page while having originally masqueraded as a Wiki site—hence the malware's moniker, "WikiLoader."
The extra shell code at the designated offset in the C2 server's response was empty at the time of examination. Still, there is reason to be concerned about the possibility of more nefarious activity. The fact that the C2 server's URLs are still reachable suggests that the threat actors could modify their strategy or update the payload at any time.
This malware's discovery is a clear reminder of how important it is to always download software from official distribution sites. Users are advised to proceed with the utmost caution when working with cracked software or software obtained from unidentified sources. Users of Notepad++ are strongly encouraged to upgrade their software from the official Notepad++ website and confirm the integrity of their installations, as the security community is actively working to address this problem.
It's also advised to use a reliable antivirus tool to perform a thorough system scan to make sure the malware has been completely eradicated. This incident emphasizes how cyber risks are constantly changing and how important it is to maintain ongoing attention in the digital world. To defend against such sneaky assaults, users and organizations need to be well-informed and have strong security procedures.
Impact
- Code Execution
- Unauthorized Access
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- c4ac3b4ce7aa4ca1234d2d3787323de2
- 6136ce65b22f59b9f8e564863820720b
- fe4237ab7847f3c235406b9ac90ca845
- d29f25c4b162f6a19d4c6b96a540648c
- 8b7a358005eff6c44d66e44f5b266d33
- d5ea5ad8678f362bac86875cad47ba21
SHA-256
- 4552e84edd73799b3a6e8e6d8ad0cb231d44241748ecb072c82ee9211728236c
- a001642046a6e99ab2b412d96020a243a221e3819eaac94ab3251fad7d20614b
- 2da2fcd61d20eb6f842d833e7fd5ccc6c2aadde908b6e435cd1c94d469aad5ce
- 5af95489c5c3c6e2643a4218543e6e39b62ed6c5b4c97cef9c812ba913d4f7f2
- c6c250e1cd6d5477b46871ffe17deac248d723ad45687fc54ae4fc5e3f45d91c
- fbd959e9578a01c763fd72bec06c8a3bf6683800d587bfd46cc8abe8342c80b9
SHA1
- e11ae6392aebab8a878bf4bfa3f6e68ced0c6658
- 2e4b1e2bbe9ec23d9b1d83a800c06afdf4aafa12
- fc86d79e67ebe6352343ce370c7ff32711171af9
- 12c8d43af0077c400fdf4d3e9c83fcef6111ba57
- a8473f2db5cc7d2cba76416be23d7c55fc38c8dc
- a9f9d07bc8a020ab42db8d217a8df8d334a3febb
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Be vigilant when downloading software and double-check the URL to see if it is legitimate.
- Never download software from untrusted sources.
- Download apps only from official app stores like Google Play Store or Apple App Store. Avoid downloading apps from third-party websites or unofficial sources.
- Review the permissions requested by apps before installing them. Be cautious of apps that request unnecessary permissions or access to sensitive data.
- Do not download documents attached in emails from unknown sources and strictly refrain from enabling macros when the source isn’t reliable.
- Keep your operating system and apps up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions on time. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets.
- Along with network and system hardening, code hardening should be implemented within the organization so that their websites and software are secure. Use testing tools to detect any vulnerabilities in the deployed codes.
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Be cautious of unsolicited messages, emails, or links, especially from unknown or suspicious sources. Avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from untrusted sources.
- Patch and upgrade any platforms and software timely and make it into a standard security policy. Prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities and zero-days.
- Regularly backup your data to a secure location, such as a cloud storage service or external hard drive.
- Develop and regularly update an incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in case of a security breach. Test the plan through simulations to ensure its effectiveness.

