Severity
High
Analysis Summary
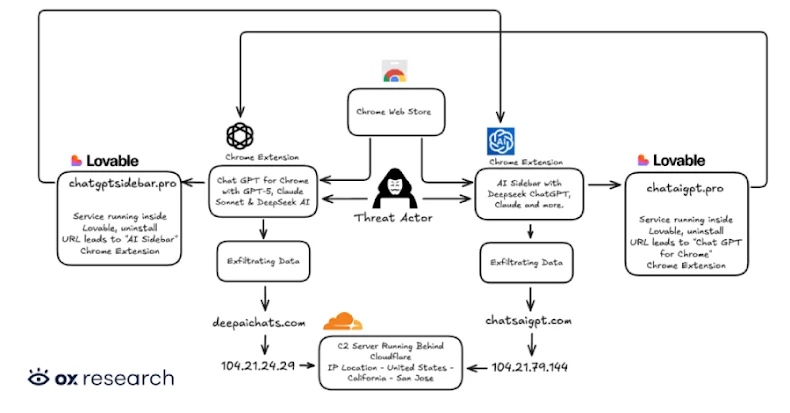
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a growing threat dubbed “Prompt Poaching,” where malicious and even legitimate browser extensions secretly collect AI chatbot conversations and browsing data. Two newly discovered malicious Chrome extensions were found exfiltrating conversations from OpenAI ChatGPT and DeepSeek, along with users’ open tab URLs, to attacker-controlled servers every 30 minutes.
The extensions, “Chat GPT for Chrome with GPT-5, Claude Sonnet & DeepSeek AI” (600,000 users) and “AI Sidebar with Deepseek, ChatGPT, Claude, and more” (300,000 users), together had over 900,000 installations. They masqueraded as a legitimate extension from AITOPIA and requested permission for “anonymous analytics,” while covertly stealing full conversation content. The harvested data was sent to remote command-and-control servers such as chatsaigpt[.]com and deepaichats[.]com. As of reporting, both extensions remained available on the Chrome Web Store, though one lost its “Featured” badge.
The malware operates by scanning specific DOM elements within chatbot webpages to extract messages, storing them locally before exfiltration. Threat actors also used AI-powered web platforms like Lovable to host privacy policies and infrastructure, adding a layer of obfuscation.
Beyond malicious add-ons, researchers found that legitimate extensions are also engaging in prompt poaching. Security researchers reported that Similarweb and Stayfocusd, with millions of users combined, collect AI inputs and outputs through disclosed policy updates. Similarweb explicitly states it gathers prompts, queries, uploaded files, and chatbot outputs to provide analytics, using DOM scraping and hijacked browser APIs such as fetch() and XMLHttpRequest().
The implications are severe. Stolen AI conversations and browsing data may expose intellectual property, internal corporate URLs, customer data, and sensitive business discussions, enabling corporate espionage, identity theft, targeted phishing, or underground resale.
Researchers warn this trend is accelerating as extension developers seek new monetization methods. Users and organizations are strongly advised to remove suspicious extensions, carefully review permissions and privacy policies, and avoid installing add-ons from unknown or misleading sources, even if they appear popular or “featured.”
Impact
- Identity Theft
- Data Exfiltration
- Cyber Espionage
- Unauthorized Access
- Sensitive Information Theft
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- chataigpt.pro
- chatgptsidebar.pro
- deepaichats.com
- chatsaigpt.com
- deepseek.ai
- chatgptbuddy.com
MD5
2ca5fe66e487646b5386292ba7b29995
72f3caa749211c4ea3b9a23065141abd
SHA-256
98d1f151872c27d0abae3887f7d6cb6e4ce29e99ad827cb077e1232bc4a69c00
20ba72e91d7685926c8c1c5b4646616fa9d769e32c1bc4e9f15dddaf3429cea7
SHA1
5ba3ae7e023f5c886a90ccafdc0a1edd0d380198
1ce608d79286d1da3fcc3ed218237f9a2a4415f0
Remediation
- Remove untrusted or unnecessary browser extensions immediately to eliminate active data collection risks
- Audit extension permissions regularly and revoke access that exceeds the extension’s core functionality
- Restrict AI tool usage on corporate browsers through policy-based controls and managed profiles
- Monitor outbound network traffic for suspicious connections to unknown or newly registered domains
- Enforce browser extension allow-lists in enterprise environments to limit installations to vetted add-ons
- Educate users about prompt sensitivity and discourage sharing confidential or proprietary data with AI tools
- Keep browsers and security tools up to date to reduce exposure to known exploitation techniques
- Use endpoint security solutions capable of detecting DOM scraping and malicious browser behavior


