Severity
High
Analysis Summary
The SocGholish malware, also known as FakeUpdates, is being used in a sophisticated campaign to deploy both a remote access trojan (RAT) called AsyncRAT and an open-source project known as BOINC.
BOINC, the Berkeley Open Infrastructure Network Computing Client, is a legitimate "volunteer computing" platform designed to leverage the power of participating home computers for large-scale distributed computing tasks. Managed by the University of California, BOINC allows users to contribute their computing resources to various scientific projects and rewards participants with a specific type of cryptocurrency called Gridcoin.
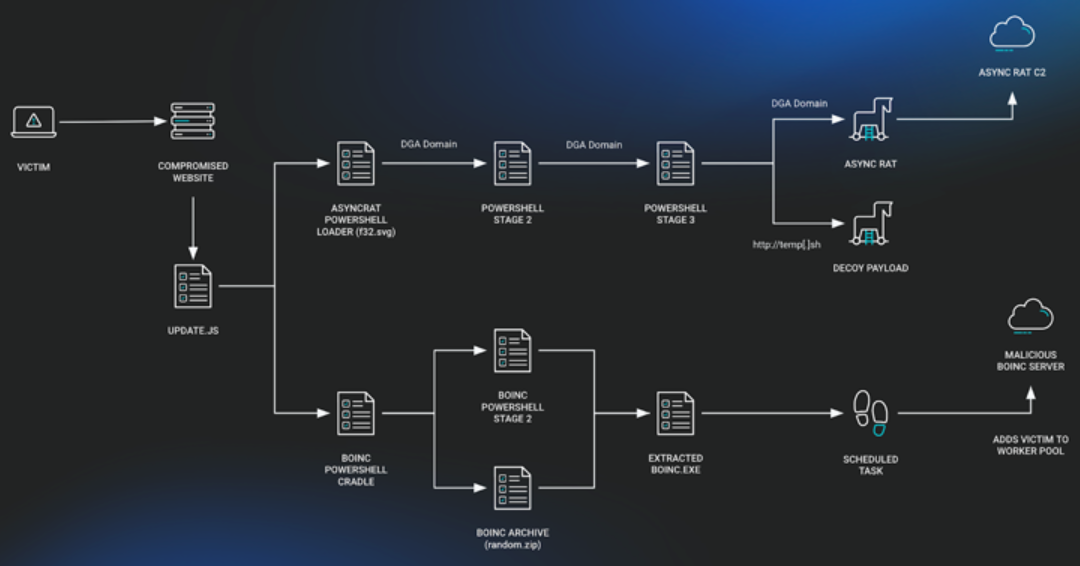
However, cybersecurity researchers have discovered that the SocGholish campaign is exploiting BOINC for malicious purposes. Infected machines connect to domains controlled by the threat actors which function as command-and-control (C2) servers. These servers collect host data, transmit additional malicious payloads, and push further commands. As of mid-July 2024, over 10,000 clients are reported to be connected to these malicious domains.
The attack begins with users landing on compromised websites where they are tricked into downloading a fake browser update. This download initiates two separate payload chains, one deploys a fileless variant of AsyncRAT, and the other installs BOINC. To avoid detection, the BOINC application is renamed to common Windows service names like "SecurityHealthService.exe" or "trustedinstaller.exe" and sets up persistence via a scheduled task created by a PowerShell script.
The misuse of BOINC in this manner has not gone unnoticed. The project maintainers are actively investigating the issue to find ways to prevent this form of abuse. Although no follow-on malicious activities have been observed from the infected hosts, researchers hypothesize that the threat actors could sell the host connections as initial access points to other malicious actors potentially leading to ransomware attacks.
The potential risk posed by this abuse of BOINC is significant. Infected clients connecting to malicious servers could allow threat actors to execute various malicious commands, escalate privileges, move laterally within a network, and compromise entire domains. This development highlights an ongoing trend noted by cybersecurity firms where malware authors are increasingly using sophisticated methods such as compiled V8 JavaScript to evade static detections and conceal a range of malicious activities including RATs, stealers, loaders, cryptocurrency miners, wipers, and ransomware.
The continuous evolution of malware techniques, such as the use of V8 JavaScript, underscores the relentless arms race between security experts and threat actors. As malicious developers adopt and adapt new technologies to hide their activities and bypass security measures, the importance of vigilant and adaptive cybersecurity practices becomes ever more critical. The current situation with BOINC serves as a stark reminder of the need for ongoing vigilance and innovation in the cybersecurity field.
Impact
- Unauthorized Access
- Exposure of Sensitive Data
- Command Execution
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- rosetta.top
- rosetta.cn
- rzegzwre.top
- klmnnilmahlkcje.top
- ga1yo3wu78v48hh.top
IP
- 64.7.199.144
- 216.245.184.105
- 5.161.214.209
- 104.200.73.68
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions promptly. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets.
- Patch and upgrade any platforms and software on time and make it into a standard security policy.
- Employ network intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor and block malicious network activities.
- Implement network segmentation to limit lateral movement for attackers within the network.
- Implement advanced email filtering to detect and block phishing emails.
- Employ updated and robust endpoint protection solutions to detect and block malware.
- Develop and test an incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective response to security incidents.
- Enhance logging and monitoring capabilities to detect anomalous activities and unauthorized access.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Regularly back up critical data and ensure that backup and recovery procedures are in place.

