Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Researchers have uncovered a sophisticated cybercriminal campaign named "Tusk" orchestrated by Russian-speaking threat actors. The campaign involves impersonating legitimate brands to distribute malware like DanaBot and StealC.
According to the researchers, Tusk comprises several sub-campaigns that utilize social engineering tactics like phishing to deceive victims into downloading malware through bogus websites and social media accounts. Notably, these sub-campaigns leverage reputable platforms like Dropbox to host the initial downloaders designed to deliver additional malware samples to the victim's machine.
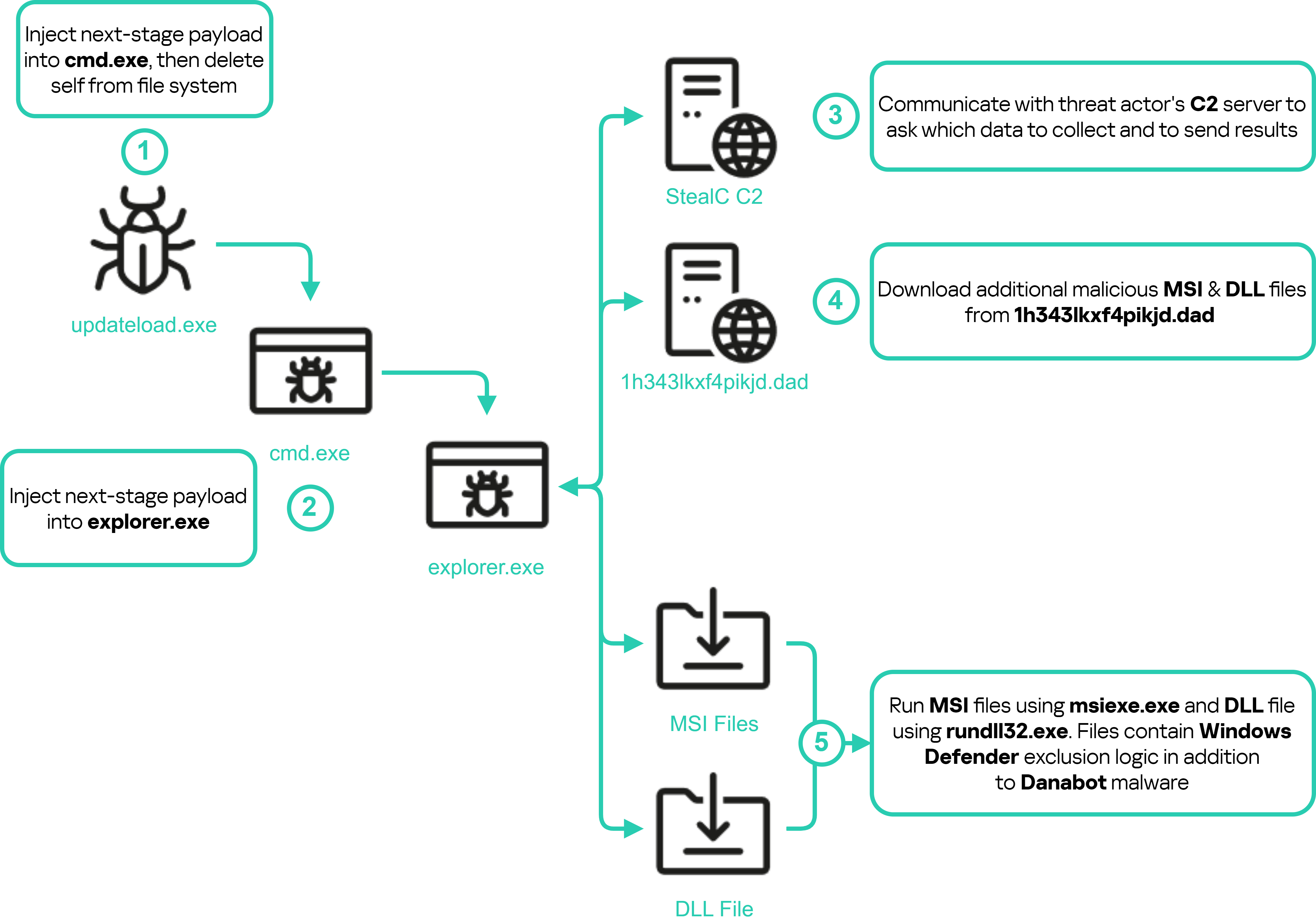
Among the 19 identified sub-campaigns, three are currently active. The first, named TidyMe, mimics the website peerme[.]io and hosts lookalike sites (tidyme[.]io, tidymeapp[.]io, and tidyme[.]app). These sites prompt users to download a malicious Electron application for Windows and macOS. The application after requiring a CAPTCHA input covertly fetches and executes additional malicious files in the background, eventually deploying the StealC malware to harvest a wide range of information from the victim’s system.
The second active sub-campaign, RuneOnlineWorld, involves a fake website ("runeonlineworld[.]io") that mimics an MMO game called Rise Online World. This site distributes a downloader that installs both DanaBot and StealC on compromised hosts. The campaign also employs a Go-based clipper malware designed to monitor and manipulate clipboard content specifically targeting Bitcoin wallet addresses to perform fraudulent transactions.
The third sub-campaign, Voico, impersonates an AI translator project called YOUS with a malicious counterpart hosted on voico[.]io. This downloader prompts victims to fill out a registration form, capturing their credentials before logging them onto the console. Like the other sub-campaigns, it deploys StealC malware, although it communicates with a different command-and-control (C2) server. Overall, these campaigns demonstrate the advanced capabilities of the threat actors who exploit users' trust in well-known platforms to steal sensitive information and achieve financial gain.
Impact
- Sensitive Data Theft
- Cyber Espionage
- Credential Theft
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- tidyme.io
- tidyme.app
- tidymeapp.io
- runeonlineworld.io
IP
- 46.8.238.240
- 77.91.77.200
- 23.94.225.177
MD5
- ecc1bf63f540d20347dda8ddb33f3155
- 53389c573687c3162b8f75dd73168c08
- 9152b6bd1ce59c0ece04db6a3be2d5fd
- 3762687f6636ac9f2cbf99aa7a15cd46
- f3e0af731513886c7588780b3350924c
- 68bced64ec1e8f57243c4f04e8fc5fb0
- e036a20d879b669bf96f17a6f17f4c4d
- 8b2d78aa6df535841b943b4d1745352e
SHA-256
- 0d877b9163241e6d2df2779d54b9eda8abc909f022f5f74f084203134d5866e2
- 142b8d0080db24246615059e4badf439f68c2b219c68c7ac7f4d2fc81f5bb9c2
- 1f3aa94fb9279137db157fc529a8b7e6067cbd1fe3eb13c6249f7c8b4562958a
- 5535bf554c8314b500fb9f00d5bdea0ade884cb7c74536bdaafa501361232e73
- 592052016d9621eb369038007ab13b19632b7353fafb65bd39268796d5237c8c
- 609129a9188ca3d16832594d44d746d7434e67a99c6dd20c1785aface9ed117d
- d69a93df6cab86b34c970896181bb1b618317e29ca8b5586364256a1d02b7cca
- 6cc3e6b74d2018ce3d86e6e9df2846a14cc980e8f95779b3ce4e83bb1ccd72bd
SHA-1
- d28a179fb39d1487034e4f26d3e4d528e9c9d04b
- 19d399bd72ad9dfb80cc4952e025c448849533ab
- e02f3f2ff8da78a59e1b2208852c9873f9b27b34
- fef00ffe364e45fb33034609a3cf60f7653af2aa
- ff855a30017ffc59c885745fdb716217b777e666
- f1719b1cf427afb31f91789e8fef8cbd77c5a613
- 95eaeb5d63da9766590e2b3c38fc98b46eb321b0
- 54658838e1d841d9aee4608a588884f441020710
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Regularly update all software and systems to ensure vulnerabilities are patched promptly.
- Implement robust email filtering to block phishing attempts that may deliver initial infection loaders.
- Utilize advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools to identify and block suspicious activities.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and mitigate potential security gaps.
- Employ least privilege principles, ensuring users and applications have the minimum necessary access rights.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add a layer of security to user accounts.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual activities that could indicate the presence of malware or unauthorized access.
- Educate employees on recognizing phishing emails and safe online practices to reduce the risk of initial infection.
- Establish and test incident response plans to ensure rapid containment and recovery in the event of ransomware.
- Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.
- Implement multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security to login processes.

