Severity
High
Analysis Summary
The emergence of the Cuttlefish malware represents a significant threat to both enterprise-grade and small office/home office (SOHO) routers, demonstrating a sophisticated capability to monitor and exfiltrate data while evading traditional security measures.
Cybersecurity researchers' analysis reveals that Cuttlefish operates stealthily by creating proxy or VPN tunnels on compromised routers, allowing attackers to discreetly siphon off sensitive information without detection. Furthermore, the malware's ability to perform DNS and HTTP hijacking within private IP spaces adds another layer of complexity, potentially facilitating the introduction of additional malicious payloads.
While Cuttlefish shares some code similarities with HiatusRat, which has been associated with Chinese state interests in the past, attributing the malware to any specific actor remains challenging. Despite this overlap, there is currently no concrete evidence linking Cuttlefish to any known threat actor. However, researchers have traced Cuttlefish's activity back to at least July 2023 with a recent concentration of infections primarily observed in Turkey, albeit with some impact on satellite phone and data center services elsewhere.
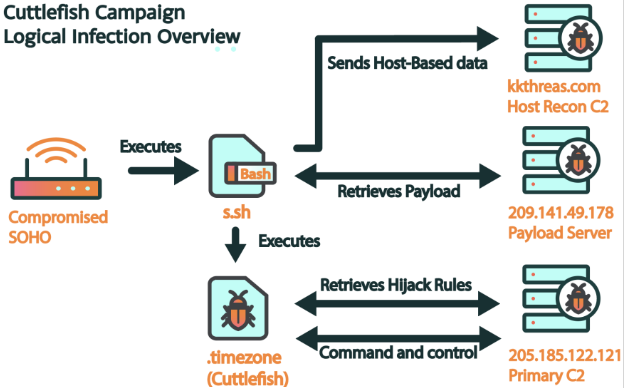
The infection chain of Cuttlefish begins with the initial compromise of routers, which may involve exploiting known vulnerabilities or brute-forcing credentials. Once access is gained, a bash script is deployed to collect host-based data and execute the primary Cuttlefish payload which is loaded into memory to evade detection. The malware's versatility is highlighted by its availability in various builds supporting multiple router architectures ensuring widespread compatibility and effectiveness.
Cuttlefish's modus operandi involves monitoring all connections through the compromised device, actively sniffing for credential markers within the traffic, particularly targeting public cloud-based services such as Alicloud, AWS, and CloudFlare. Upon detection, the malware logs the relevant data locally before exfiltrating it to the command and control server using peer-to-peer VPN or proxy tunnels. Additionally, Cuttlefish possesses the capability to manipulate DNS and HTTP requests redirecting traffic to actor-controlled infrastructure and potentially hijacking internal or site-to-site communications.
To mitigate the threat posed by Cuttlefish, organizations are advised to strengthen their security posture by eliminating weak credentials monitoring for unusual logins securing traffic with TLS/SSL, and inspecting devices for rogue configurations. Regularly rebooting devices, applying firmware updates, changing default passwords, and blocking remote access to management interfaces are also recommended measures, particularly for SOHO router users.
Impact
- Credential Theft
- Data Exfiltration
- Security Bypass
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- kkthreas.com
MD5
- 2abe840c10755c2571bddf2abea537f2
- b2ca9e24000c6b5846ffecd70083a850
- c123c4426418dd329d6f306582ac9dd5
- 9b7a35a728924ca782e77a68d281c777
- edfebb4e48c4681c89b3ac6b370cf88b
SHA-256
- 73cf20675639c18c04381b5efd7d628736d149734280988f55358e301c1d9bb8
- 10a4edbbb852a1b01fc6fbf0aa1407bc8589432bddb2001ae62702f18d919e89
- 94812d391160e4fce821701b944cfd8f5fd9454b3cbb8e8974d1dc259310e500
- 4aa23fbdc27d317c6e54481b6d884b962adf6e691a4731c859ddaf9af09822c6
- 1168e97ccf61600536e93e9c371ee7671bae4198d4bf566550328b241ec52e89
SHA1
- 114419df7296c38dda5b7c52fab3e16e89c472ba
- 8c92790a1a630d8e27a33bcfbb634b2f56f5dcd1
- eb6b765180c8b46fddc1a43d2c9a82591b6d2ea9
- b6195aec010f77a8b53a74a3caa161fdc06dcf32
- 2773ee18bc041f6d8e95af46bc5212529853a347
URL
- http://209.141.49.178/s
- http://209.141.49.178/dajfdsfadsfa/arm
- http://209.141.49.178/dajfdsfadsfa/i386
- http://209.141.49.178/dajfdsfadsfa/i386_i686
- http://209.141.49.178/dajfdsfadsfa/i386_x64
- http://209.141.49.178/dajfdsfadsfa/misp32
- http://209.141.49.178/dajfdsfadsfa/misp64
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Ensure that general security policies are employed including implementing strong passwords, correct configurations, and proper administration security policies.
- Patch and upgrade any platforms and software timely and make it into a standard security policy. Prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities and zero-days.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions on time. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets.
- Never open links or attachments from unknown senders.

