Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Rilide, a sophisticated browser-based malware, has emerged as a major threat targeting Chrome and Edge users through deceptive browser extensions. It primarily spreads via phishing emails containing fake browser update links or compromised websites that trick users into installing the malicious extension. Once installed, Rilide requests extensive permissions, enabling it to monitor browser activity, intercept form submissions, and establish persistence by creating a background service worker that remains active even after a browser restart. Security researchers have identified this malware in active campaigns across North America and Europe, with widespread credential theft incidents reported at financial institutions and e-commerce platforms.
The malware exhibits advanced obfuscation techniques to bypass browser security checks and extension verification, making detection highly challenging. It communicates with multiple command-and-control (C2) servers using encrypted protocols, as discovered by Researcher, who tracked unusual data exfiltration patterns. Rilide has the capability to capture login credentials from over 300 websites, including banking portals and cloud services, making it particularly dangerous for corporate environments. Once an account is compromised, attackers can leverage lateral movement within a network, increasing the severity of the breach. The infection has already resulted in approximately 75,000 installations worldwide since its discovery in early March.
Rilide’s infection mechanism relies on extensive permission requests in its manifest file, including access to tabs, storage, web requests, cookies, and background script execution. The credential theft functionality is embedded in the content script, which injects event listeners to capture user input before encryption, effectively bypassing HTTPS security. This allows attackers to steal login credentials in real-time before they are securely transmitted. Additionally, the malware includes dormancy features to evade detection, as well as mechanisms to detect security analysis environments and alter its behavior accordingly.
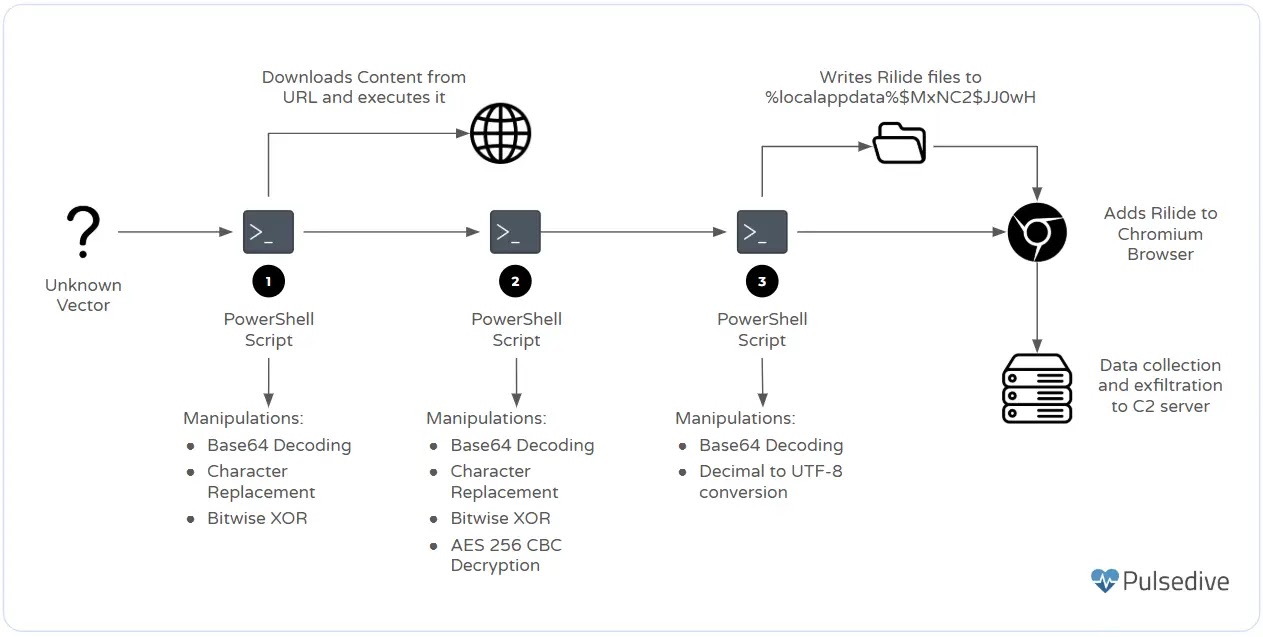
To mitigate the risk posed by Rilide, security researchers recommend strict browser extension management, blocking unauthorized installations, and enabling PowerShell logging to detect suspicious activity. Organizations should also enforce policies that restrict users from executing PowerShell commands, as attackers often use it for post-exploitation activities. Given the rapid spread and sophisticated evasion tactics of Rilide, security teams must remain vigilant against emerging threats that exploit browser vulnerabilities for credential theft and unauthorized access.
Impact
- Credential Theft
- Security Bypass
- Gain Access
- Financial Loss
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- ashgrrwt.click
- tcl-black.com
- nch-software.info
- nvidia-graphics.top
- vceilinichego.ru
- web-lox.com
- assets.bnbcoinstatic.com
- proyectopatentadomxapostol.com
- blackfox.lol
- pupkalazalupka.com
- extension-login.com
- tes123123t.com
- extensionsupdate.com
- nightpredators.com
IP
45.15.156.210
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Allow only trusted and verified extensions to be installed through centralized IT policies.
- Monitor and log all PowerShell activity to detect potential threats and unauthorized script execution.
- Restrict users from running PowerShell commands unless explicitly required for work purposes.
- Implement MFA for all critical accounts to prevent unauthorized access even if credentials are compromised.
- Use security solutions to detect unusual data exfiltration patterns linked to C2 communications.
- Ensure endpoint protection software and web filters block access to malicious sites distributing fake browser updates.
- Conduct regular security awareness training to help users recognize and avoid phishing emails and fake browser update prompts.
- Conduct periodic security audits to identify and remove any suspicious or unauthorized browser extensions.
- Deploy EDR solutions to detect and mitigate malware-based threats targeting browser vulnerabilities.
- Keep all web browsers up to date with the latest security patches to minimize exploitation risks.

