Severity
High
Analysis Summary
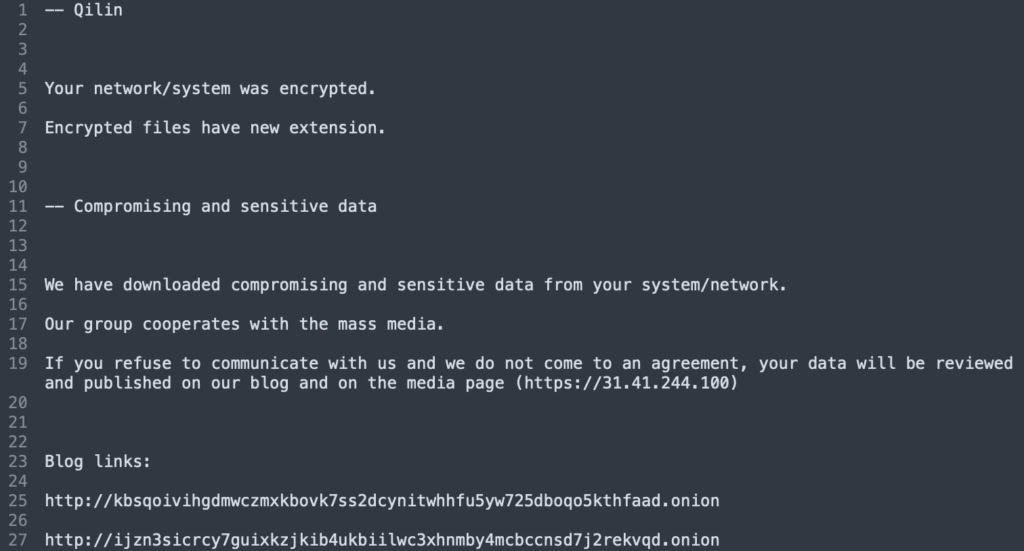
Qilin ransomware, formerly known as Agenda, is a Russian-speaking ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation that emerged in July 2022. Known for its high adaptability, Qilin enables affiliates to customize attacks, targeting both Windows and Linux/ESXi systems. It employs double extortion tactics, encrypting files and exfiltrating data to pressure victims into paying ransoms. Initial access is typically achieved through phishing emails, exploitation of known vulnerabilities, or compromised RDP and VPN credentials. Qilin uses various evasion methods, including disabling event logs and booting systems into Safe Mode to bypass security tools.
In 2024–2025, Qilin launched several major campaigns, including a high-impact ransomware attack on Synnovis, a UK-based healthcare provider, affecting NHS hospitals and compromising up to 300 million patient records. It has also targeted municipal systems in the U.S. and educational institutions, with victims across healthcare, manufacturing, education, government, critical infrastructure, and technology sectors. Countries affected by Qilin include the United Kingdom, United States, France, Brazil, Germany, Japan, Australia, and the UAE. Although sophisticated, Qilin is not attributed to any nation-state APT group and is classified as a financially motivated cybercrime group, making it a growing global threat to essential services and critical infrastructure.
Impact
- Exposure of Sensitive Information
- Operational Disruption
- Financial Loss
- Reputational Damage
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
f6f89e070ed9be62b9ca284f2f7af9e5
b7190b72bc8ff87f5bddd87de01f3343
SHA-256
d3af11d6bb6382717bf7b6a3aceada24f42f49a9489811a66505e03dd76fd1af
aeddd8240c09777a84bb24b5be98e9f5465dc7638bec41fb67bbc209c3960ae1
SHA1
b7b6e89c037599c2111093fabeee04c6b9333ceb
fa62188bdcbfdb784665c08e57d7072511ee9465
Remediation
- Isolate infected systems immediately to contain the threat
- Disconnect affected devices from the internet and local networks
- Block all known indicators of compromise across security controls
- Conduct a full forensic investigation to determine the scope of the attack
- Use reputable antivirus or EDR tools to remove the ransomware
- Restore encrypted files from clean, offline backups
- Reset all user credentials, especially for administrative accounts
- Patch all exploited vulnerabilities in systems and applications
- Enable multi-factor authentication across all critical systems
- Implement network segmentation to limit lateral movement
- Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing
- Educate employees about phishing and social engineering risks
- Monitor system logs and network traffic for unusual activity
- Develop and test an incident response and disaster recovery plan
- Regularly back up important data and store it in secure, isolated environments

