Severity
High
Analysis Summary
NGate is a newly discovered Android malware capable of stealing money from payment cards by relaying NFC (Near-Field Communication) data to an attacker's device. This allows attackers to emulate victims' cards, enabling unauthorized payments or cash withdrawals from ATMs.
The NGate campaign has been active since November 2023, primarily targeting users in Czechia. It is linked to a broader phishing campaign involving Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and advanced WebAPKs that steal banking credentials. The malware has been used in several cases to perform direct cash theft.
The attacks typically begin with malicious texts, automated calls, or malvertising that trick victims into installing a malicious PWA, which later escalates to WebAPKs. These apps, disguised as urgent security updates, mimic the official icons and login interfaces of targeted banks to steal client credentials. Once the phishing phase is completed, victims are prompted to install NGate.
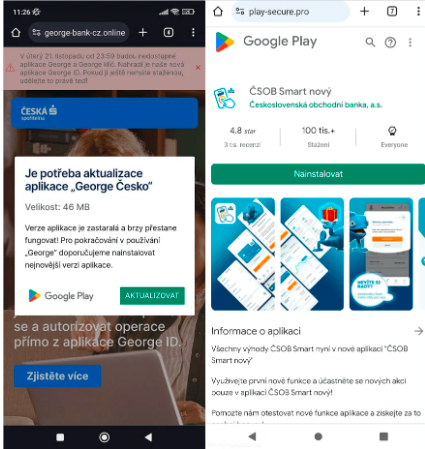
NGate activates an open-source component called NFCGate, originally developed for NFC testing. This tool captures NFC data from payment cards near the infected device and relays it to the attacker, who can then use the data for unauthorized transactions or cash withdrawals at ATMs.
For most ATM withdrawals, the attacker needs the card's PIN code. After the phishing step, scammers pose as bank employees, convincing victims to install NGate by claiming it’s a security app. Once installed, the victim is asked to scan their card and enter their PIN, which is then sent to the attacker, allowing them to complete the unauthorized transactions.
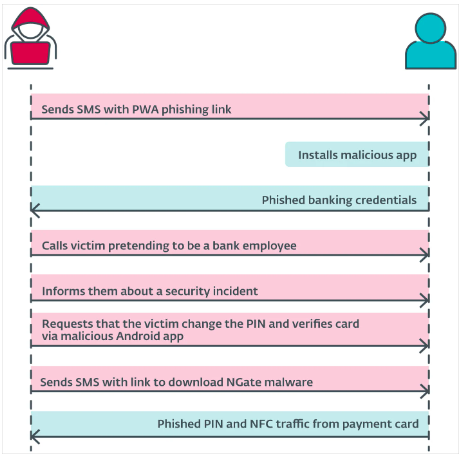
Beyond financial theft, NGate can clone NFC access cards, transport tickets, and ID badges, posing additional security risks. To mitigate these risks, users are advised to disable NFC when not in use or carefully manage app permissions. Only apps from official sources should be installed, and users should be wary of WebAPKs, which are small, browser-installed, and lack detailed information under app settings.
Google Play Protect, Android’s default malware scanner, detects NGate and has confirmed that no apps containing this malware are present on Google Play. Android users are automatically protected against known versions of NGate by default, even when apps come from outside the Play Store.
Impact
- Financial Loss
- Unauthorized Gain Access
- Sensitive Information Theft
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- raiffeisen-cz.eu
- client.nfcpay.workers.dev
- app.mobil-csob-cz.eu
- nfc.cryptomaker.info
IP
- 91.222.136.153
- 185.104.45.51
- 185.181.165.124
MD5
- 3c7f107731634fcb7e3f07b693acd4ce
- ea6a6666616f6b02c7b679782a676eab
- 84361aaf11cde2df075e65fc31082358
- 8595855eaf9fe0398c8bff7fa06151bf
- 633c3636b646bd08af271584c0e41ff9
- 7cecbdfdf2e7a7ae7cc226ae26cd3797
SHA-256
- e19a7c8e4994ea4ed680136c9e3a6fff7b82c72f5743952821a446b6cb830f06
- ddd9e5cfa9e1ddd8d849baef2b487a1608d1695f44c70f246c101de1275887dd
- 162f8c6bafe0c343c37f173344c4f6880eaec0aea7b491565db874366b161784
- 1d126e5904dde3b46175a4aae89eec1fb8a6b80e35b1f473878e5dd288f8aae6
- 95d906dca5a3be5cf066268662b3c953860e54e9cdcfcd427faf0aaa9cb62bad
- 17a16f08108e25af1c8b058adbaca2cada6a93c2d38c9854148f9e9caac76ac3
SHA-1
- 7225ed2cba9cb6c038d8615a47423e45522a9ad1
- 66de1e0a2e9a421dd16bd54b371558c93e59874f
- da84bc78ff2117ddbfdcba4e5c4e3666eea2013e
- e7ae59cd44204461edbddf292d36eeed38c83696
- 103d78a180eb973b9ffc289e9c53425d29a77229
- 11be9715be9b41b1c8527c9256f0010e26534fdb
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Regularly change passwords for all accounts and use strong, unique passwords for sensitive accounts.
- Carefully check the URLs before entering credentials or downloading software.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all accounts to add an extra layer of security to login processes.
- Consider the use of phishing-resistant authenticators to further enhance security. These types of authenticators are designed to resist phishing attempts and provide additional protection against social engineering attacks.
- Regularly monitor network activity for any unusual behavior, as this may indicate that a cyberattack is underway.
- Organizations need to stay vigilant and follow best practices for cybersecurity to protect their systems and data from potential threats. This includes regularly updating software and implementing strong access controls and monitoring tools.
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to respond effectively in case of a security breach or data leakage.
- Maintain regular backups of critical data and systems to ensure data recovery in case of a security incident.
- Adhere to security best practices, including the principle of least privilege, and ensure that users and applications have only the necessary permissions.
- Establish a robust patch management process to ensure that security patches are evaluated, tested, and applied promptly.
- Conduct security audits and assessments to evaluate the overall security posture of your systems and networks.
- Implement network segmentation to contain and isolate potential threats to limit their impact on critical systems.
- Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.

