Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Threat hunters have discovered a campaign targeting Fortinet FortiGate firewall devices with exposed management interfaces on the public internet. Beginning in mid-November 2024, unknown attackers gained unauthorized access to these devices, exploiting what is suspected to be a zero-day vulnerability. They altered configurations, created administrative accounts, and leveraged SSL VPN access for lateral movement using a technique called DCSync to extract credentials.
Researchers noted the campaign involved extensive use of the jsconsole interface from unusual IP addresses, possibly indicating the involvement of multiple threat actors. The attack consisted of four phases:
- Reconnaissance
- Configuration Changes
- Creation of Super Admin Accounts
- Lateral Movement
Attackers created super admin accounts, added new local user accounts, and modified firewall settings. In some cases, existing accounts were hijacked and granted VPN access. The threat actors also set up new SSL VPN portals and used virtual private servers (VPS) to establish SSL VPN tunnels with the compromised devices. The campaign appeared opportunistic, targeting diverse organizations without specific sectors or sizes.
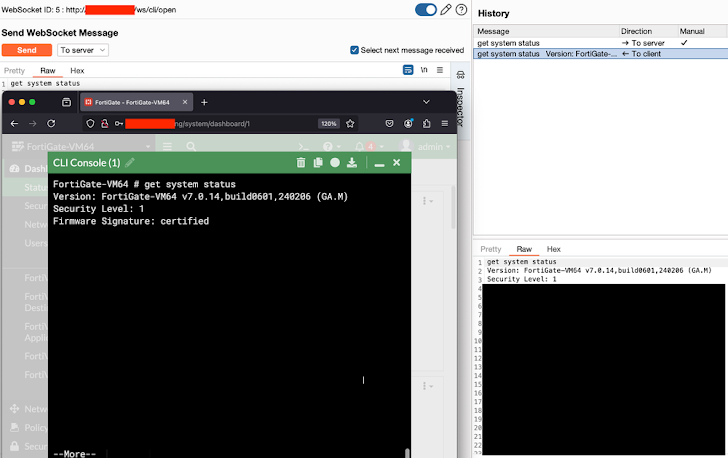
Fortinet confirmed the exploitation of a critical authentication bypass vulnerability (CVE-2024-55591) in FortiOS and FortiProxy, assigned a CVSS score of 9.6. The vulnerability allows remote attackers to gain super admin privileges via crafted WebSocket requests to the Node.js module. This flaw affects FortiOS versions 7.0.0 through 7.0.16 and FortiProxy versions 7.0.0 through 7.0.19, among others. The company urged customers to upgrade to patched versions (FortiOS 7.0.17 or above, FortiProxy 7.0.20 or above) and implement mitigation measures such as avoiding public exposure of management interfaces.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added CVE-2024-55591 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, requiring federal agencies to apply fixes by January 21, 2025. Fortinet has been actively coordinating with government and industry partners, emphasizing timely patching and network monitoring to mitigate risks.
A proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2024-55591 was released by researcher on January 28, 2025. Researchers identified a series of flaws enabling exploitation, including the ability to initiate WebSocket connections from pre-authenticated HTTP requests, bypass session checks using a local access token, and exploit race conditions between the WebSocket and Telnet-based CLI process. These issues allow attackers to establish authenticated WebSocket connections and assign themselves super admin privileges.
According to the an analysis, nearly 45,000 hosts remain vulnerable to CVE-2024-55591 as of January 27, 2025, though this number has decreased from approximately 52,000 ten days earlier. The exploitation of this vulnerability underscores the importance of maintaining up-to-date firmware, monitoring for unusual activity, and limiting public access to critical infrastructure management interfaces.
In addition to immediate remediation efforts, organizations should adopt proactive cybersecurity measures, including timely patching, access controls, and threat intelligence monitoring, to defend against evolving threats targeting critical infrastructure.
Impact
- Unauthorized Gain Access
- Security Bypass
Indicators of Compromise
IP
23.27.140.65
66.135.27.178
45.55.158.47
167.71.245.10
137.184.65.71
155.133.4.175
37.19.196.65
64.190.113.25
Remediation
- Refer to FortiGuard Advisory for patch, upgrade, or suggested workaround information.
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Implement a robust vulnerability management program to regularly scan and identify any potential vulnerabilities in your virtualization environment. Prioritize patching and remediation based on criticality and impact.
- Implement network segmentation to isolate critical systems from other less critical systems. This can help contain the impact of a potential compromise and limit lateral movement within the network.
- Follow the principle of least privilege for user accounts and ensure that only authorized personnel have administrative access. Regularly review and revoke unnecessary privileges to minimize the attack surface.
- Deploy robust security monitoring and intrusion detection systems to detect any suspicious activities or indicators of compromise. Implement real-time log analysis and alerting mechanisms to identify potential unauthorized access attempts.
- Educate users and system administrators about the latest threats, phishing techniques, and social engineering tactics employed by threat actors. Encourage a culture of security awareness and promote safe computing practices.

