Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Researchers have identified a previously undocumented advanced persistent threat (APT) group named LilacSquid which has been active since at least 2021.
LilacSquid has been conducting data theft campaigns targeting various industries including information technology, industrial sectors in the United States, the energy sector in Europe, and the pharmaceutical sector in Asia. The group leverages several tools in its operations, primarily the open-source remote management tool MeshAgent and a customized version of the QuasarRAT malware which researchers refer to as PurpleInk.
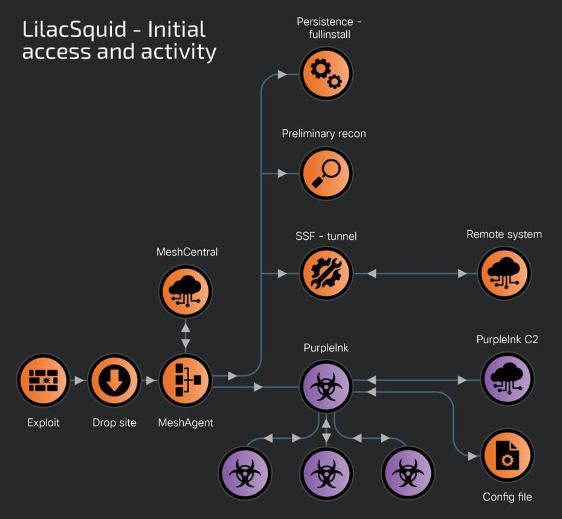
LilacSquid's primary method of attack involves exploiting vulnerabilities in Internet-facing application servers and compromising remote desktop protocol (RDP) credentials. The attackers deploy a variety of open-source tools including MeshAgent and Secure Socket Funneling (SSF), alongside customized malware such as PurpleInk, InkBox, and InkLoader. The SSF tool enables attackers to proxy and tunnel multiple sockets through a secure TLS tunnel facilitating covert communications with their command and control (C2) servers.
PurpleInk, which has been in active development since 2021, serves as the main implant for post-exploitation activities. It is heavily obfuscated and versatile, with capabilities that include enumerating processes, terminating specified processes, running new applications, gathering drive information, and exfiltrating files. PurpleInk relies on a configuration file to obtain C2 server details which are typically base64-decoded and decrypted.
The attackers use InkLoader, a .NET-based loader, to deploy PurpleInk. InkLoader is designed to run a hardcoded executable or command and supports persistence mechanisms. After a successful RDP login using stolen credentials, attackers download and install InkLoader and PurpleInk on specific directories, registering InkLoader as a service to ensure persistence. Before deploying InkLoader, the group uses another custom tool called InkBox which decrypts and runs an executable assembly from a hardcoded file path.
The researchers noted that LilacSquid’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) show significant overlap with North Korea-linked APT groups such as Andariel and Lazarus. Similar to these groups, LilacSquid uses tools like SSF and custom malware to create secure tunnels to remote servers and maintain long-term access for data exfiltration. The extensive use of these tools and the focus on establishing persistent access underscore the group's sophisticated approach to cyber espionage.
Impact
- Cyber Espionage
- Credential Theft
- Data Exfiltration
- Sensitive Information Theft
Indicators of Compromise
IP
- 67.213.221.6
- 192.145.127.190
- 45.9.251.14
- 199.229.250.142
MD5
- f81b9820f6fa7f11c8d4d223f57a579c
SHA-256
- 2eb9c6722139e821c2fe8314b356880be70f3d19d8d2ba530adc9f466ffc67d8
SHA1
- 75165906a74ad25299780e568bfac9782023d1f7
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Perform comprehensive security audits on the email server infrastructure to identify and address any potential weaknesses. This includes reviewing server configurations, access controls, and encryption protocols to ensure they meet industry best practices.
- Emails from unknown senders should always be treated with caution. Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.
- Enable 2FA for user accounts on the email server to add an extra layer of security. This prevents unauthorized access even if usernames and passwords are compromised.
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Implement network segmentation to isolate critical systems and sensitive data from the rest of the network. This limits the lateral movement of attackers in case of a breach and reduces the impact of potential future attacks.
- Implement a regular backup strategy for email servers and critical data. Ensure that backups are stored securely and regularly tested for data restoration.
- Apply the latest security patches and updates to the email server software and associated components to address any vulnerabilities that may have been exploited by APT28. Also, prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities and zero-days.

