Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Unknown threat actors are exploiting a previously patched security flaw in Microsoft MSHTML to deliver a surveillance tool called MerkSpy, targeting users in Canada, India, Poland, and the U.S.
The campaign begins with a Microsoft Word document masquerading as a job description for a software engineer role. When opened, the document exploits CVE-2021-40444, a high-severity flaw in MSHTML that can result in remote code execution without user interaction. Microsoft addressed this flaw in its September 2021 Patch Tuesday updates.
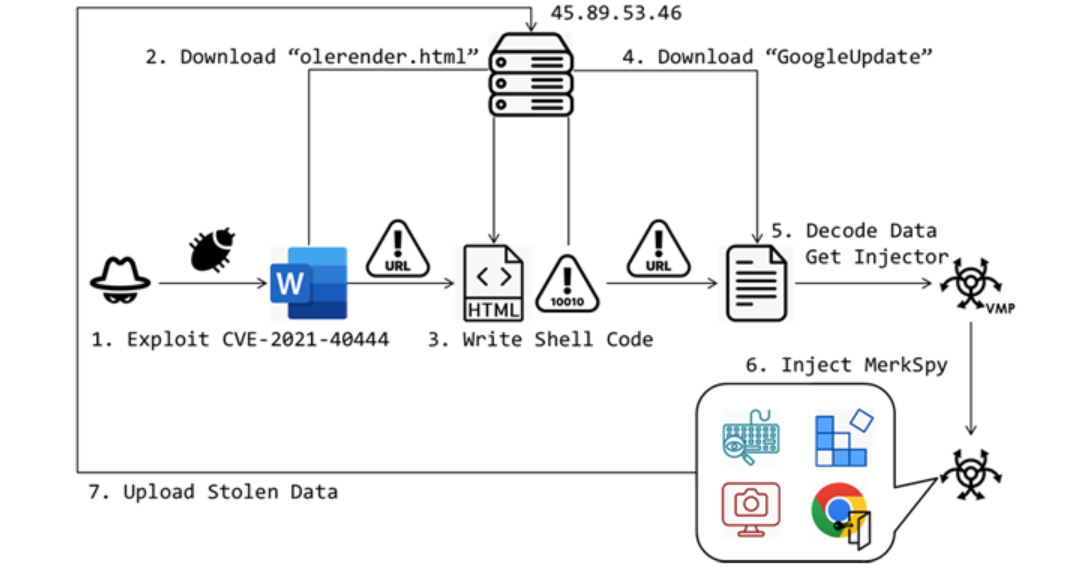
Upon exploiting the vulnerability, an HTML file named "olerender.html" is downloaded from a remote server. This file executes embedded shellcode after verifying the operating system version. The shellcode uses the 'VirtualProtect' function to change memory permissions, allowing it to securely write decoded shellcode into memory. Subsequently, 'CreateThread' executes the injected shellcode which then downloads and executes the next payload from the attacker's server ensuring seamless execution of malicious code and facilitating further exploitation.
According to the researchers, the downloaded file, deceptively titled "GoogleUpdate," contains an injector payload designed to evade security detection and load MerkSpy into memory. MerkSpy establishes persistence on the compromised system by modifying Windows Registry settings to launch automatically upon startup. The spyware captures and exfiltrates sensitive information including screenshots, keystrokes, login credentials stored in Google Chrome, and data from the MetaMask browser extension.
Additionally, researchers have reported a smishing campaign targeting U.S. users with fraudulent SMS messages claiming to be from Apple. These messages direct users to fake credential-harvesting pages disguised as legitimate Apple login pages. The malicious website includes a CAPTCHA to enhance perceived legitimacy, ultimately leading users to an outdated iCloud login template to harvest their credentials. This campaign highlights the ongoing threat landscape and the sophisticated techniques cyber criminals employ to exploit vulnerabilities and deceive users.
Impact
- Sensitive Information Theft
- Remote Code Execution
- Data Exfiltration
- Cyber Espionage
Indicators of Compromise
IP
- 45.89.53.46
MD5
- 8264e3b10d7cacd6897159459fe3dde1
- 1280cd07f63a4086ae34c55b9a09b7ae
- 321b95fdc4bcefc899f8d5802fae1edc
- e545865a9d2a4ef7689aaee289ab48fc
- 7d03cd9e630b1b514d14d78613fc98d7
SHA-256
- 92eb60179d1cf265a9e2094c9a54e025597101b8a78e2a57c19e4681df465e08
- 95a3380f322f352cf7370c5af47f20b26238d96c3ad57b6bc972776cc294389a
- 0ffadb53f9624950dea0e07fcffcc31404299230735746ca43d4db05e4d708c6
- dd369262074466ce937b52c0acd75abad112e395f353072ae11e3e888ac132a8
- 6cdc2355cf07a240e78459dd4dd32e26210e22bf5e4a15ea08a984a5d9241067
SHA1
- b26f7c569064a681f23434b6e63e31cdd1e3b761
- 742fb316e017f5e8a53d12be3d2b5a173cb089de
- 7058655f5307edba9f3925a9b508add9182259c1
- b64d2b4b478467990793bae0fa2a8282e8d4d43f
- a36c272e8967d0bb4b0c5a1110f7a81b740bbb97
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Use Microsoft Automatic Update to apply the appropriate patch for your system, or the Microsoft Security Update Guide to search for available patches.
- Apply the latest security patches and updates from Microsoft.
- Use endpoint security solutions to detect and block malicious activities.
- Educate users about the risks of opening unsolicited email attachments.
- Implement network segmentation to limit the spread of malware.
- Regularly back up data and verify the integrity of backups.
- Use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication.
- Monitor network traffic for signs of data exfiltration.
- Regularly review and update security policies and procedures.
- Implement application whitelisting to prevent unauthorized programs from executing.
- Disable or limit the use of macros in Microsoft Office documents.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
- Use advanced threat detection tools to identify and respond to malicious behavior.
- Restrict user permissions to minimize the impact of potential exploits.

