Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Operation Phantom Enigma is a highly sophisticated malware campaign uncovered by cybersecurity researchers, targeting users through malicious browser extensions.
These extensions are designed to steal sensitive banking credentials and financial data, marking a significant evolution in banking trojans. The attackers cleverly utilize browser extensions across Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Brave to bypass traditional security measures, allowing them to silently harvest authentication data from major financial institutions. The operation was discovered by a Researcher, who analyzed multiple malware samples and network infrastructure tied to the campaign.
The infection chain begins with phishing emails carrying malicious Microsoft Installer (MSI) files disguised as official government documents. Once executed, these files deploy PowerShell scripts that initiate multiple persistence mechanisms, including creating registry entries under “PWSecurity” for automatic startup and disabling User Account Control (UAC) via registry edits.
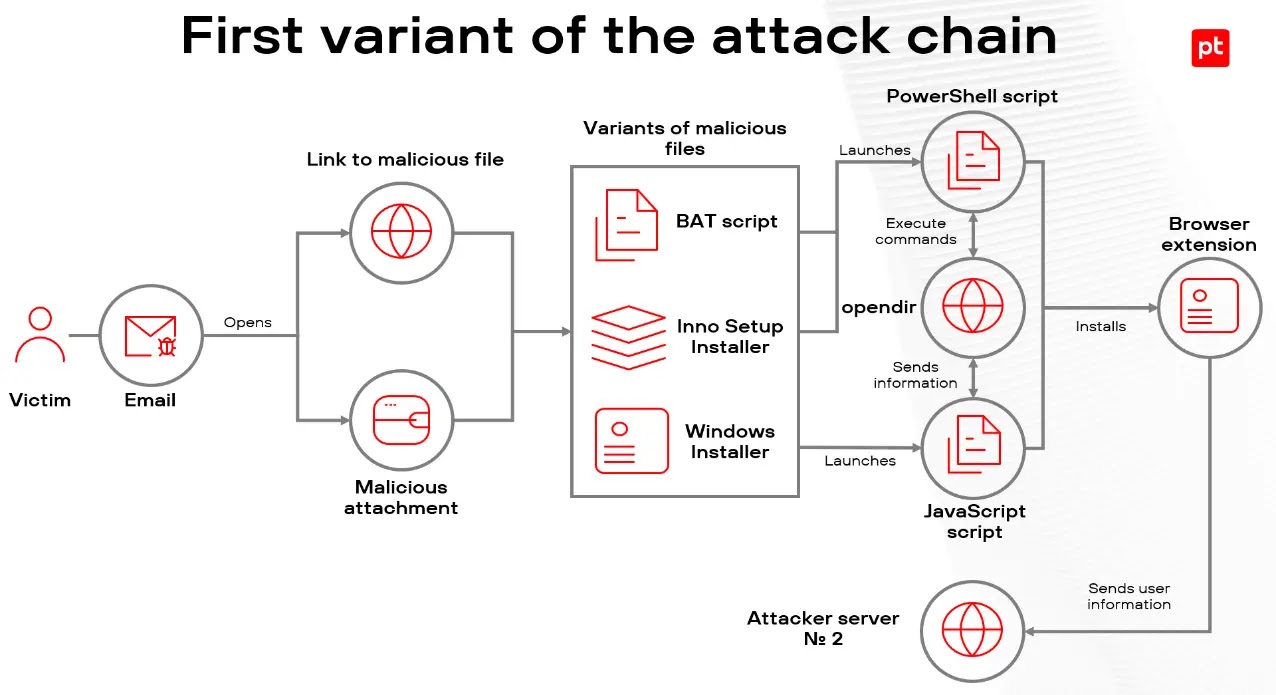
The malware employs advanced evasion techniques such as virtualization and sandbox detection using WMI queries to avoid analysis. These capabilities demonstrate an intricate understanding of system internals, enabling long-term stealth operation on infected systems.
One of the campaign’s most notable features is its tailored targeting of Brazil’s financial environment. It specifically checks for the presence of Warsaw Technology, a widely used banking security solution in Brazil—before proceeding with installation. This suggests the attackers possess deep knowledge of local banking defenses. The browser extensions are forcibly installed by modifying Chrome policy registry settings, with commands such as “START_SCREEN” and “CHECAEXT” issued from a command-and-control server at IP address 142.54.185.178 to deploy and verify the extensions' activation.
The scale of the operation is significant, with over 70 companies compromised and 722 downloads of the malicious extensions from the Chrome Web Store before takedown. Despite its current focus on Brazil, the underlying infrastructure suggests potential for expansion to other regions. The malware’s combination of phishing, registry tampering, extension-based data harvesting, and anti-analysis techniques makes it a potent and persistent threat. Operation Phantom Enigma highlights the growing threat posed by browser-based attacks and the need for enhanced monitoring of browser extensions and user endpoint defenses.
Impact
- Sensitive Credentials Theft
- Security Bypass
- Gain Access
- Financial Loss
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- atual2025.com
- clientepj.com
- computadorpj.com
- financial-executive.com
- hamrah-tejarat.com
- nfe-fiscal.com
- ranchocentral.com
- servidor2025.com
- syarousi-search.com
- nf-eletronica.org
- relay.lombrelone.com
- webrelayapi.online
IP
18.231.162.77
142.54.185.178
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Immediately disconnect any system suspected of infection from the network to prevent further data exfiltration or spread.
- Terminate malicious processes and delete persistence entries, especially registry keys like: HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\PWSecurity
- Remove unauthorized browser extensions from Chrome, Edge, and Brave by resetting browser policies and profiles.
- Disable browser extension installations via group policy unless vetted and approved by IT/security teams.
- Use Application Control solutions to block the execution of PowerShell scripts and MSI files from unknown or untrusted sources.
- Enable User Account Control (UAC) and monitor registry changes that attempt to disable it.
- Update endpoint protection tools to detect malware components, including PowerShell payloads and malicious registry activities.
- Block outbound connections to known command-and-control IP addresses, such as 142.54.185.178.
- Monitor network traffic for anomalous communications or suspicious DNS queries, especially to newly registered domains or rare IPs.
- Conduct phishing awareness training to help users recognize fake government or financial emails and avoid opening malicious MSI attachments.
- Enforce least privilege policies, users should not have administrative rights that allow unauthorized software or extension installation.
- Implement browser extension whitelisting, allowing only pre-approved extensions from trusted sources.
- Audit all user accounts for suspicious activity, especially around financial transactions and browser behavior.
- Change all banking credentials and 2FA methods on affected machines or accounts.
- Continuously monitor endpoint and server logs for re-infection attempts, and conduct threat hunting for similar malware signatures.

