Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Threat actors have been discovered using a novel method to smuggle a new malware known as RustyAttr by abusing extended attributes for macOS files. Citing tactical and infrastructure commonalities seen concerning previous campaigns, such as RustBucket, the researchers have linked the new activity with a moderate degree of confidence to the notorious Lazarus Group, which is associated with North Korea.
Extended attributes are extra metadata linked to files and directories that can be retrieved with the help of a specific command known as xattr. They are frequently used to hold data like file size, timestamps, and permissions that are not included in the normal attributes. The malicious programs found by researchers are constructed using Tauri, a cross-platform desktop application framework, and signed with a leaked certificate that has since been revoked by Apple. They feature an extended attribute that's configured to fetch and run a shell script.
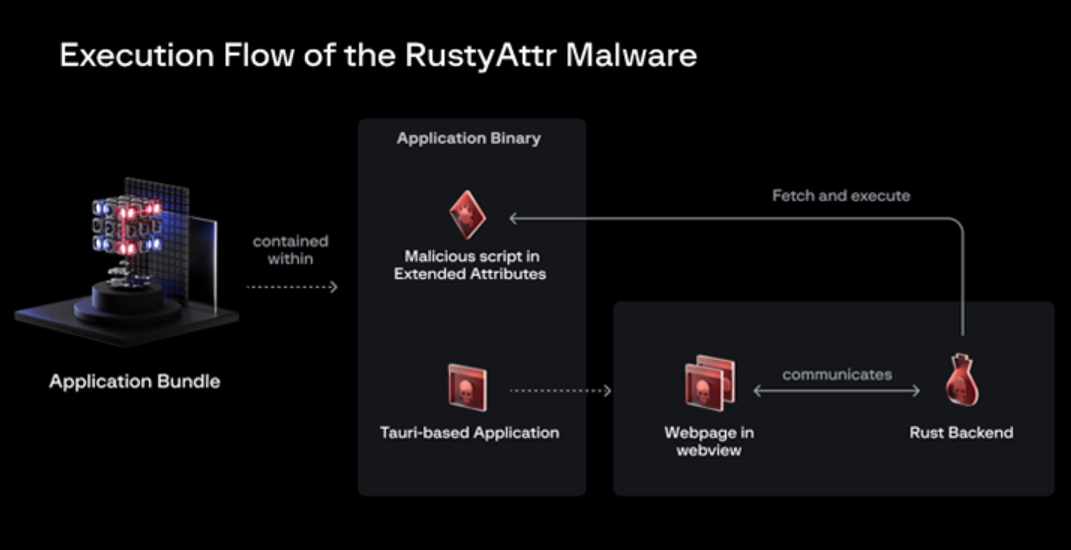
By presenting an error message such as "This app does not support this version" or an innocuous PDF document about the creation and financing of gaming projects, the shell script's execution also activates a decoy, which acts as a diversion mechanism. The threat actor utilized a random template that was downloaded from the internet, and when the application was executed, the Tauri application tried to render an HTML webpage using a WebView.
Notably, however, these websites are designed to load malicious JavaScript, which then retrieves the content of the extended attributes and runs it using a Rust backend. Despite this, the phony webpage is only shown when there are no extended attributes. The campaign's ultimate objective is still unknown, particularly since there has been no proof of any additional payloads or verified victims. Thankfully, macOS systems offer the discovered samples a certain amount of protection. Threat actors need to disable Gatekeeper by bypassing malware protection to initiate the attack. To persuade victims to take these actions, some level of contact and social engineering will probably be required.
Impact
- Code Execution
- Sensitive Data Theft
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- support.cloudstore.business
- support.docsend.site
IP
- 104.168.165.203
- 104.168.157.45
MD5
- 53b68b9304a0462761917608ca4e60e7
- 3d14dd06d85f513dfa96d875fdcc0298
- 0cbc6df98ce1d302f51714e100560a4d
- a26c2442743d234ccd3b0d104e13a798
- 3439de0b221320f58e3432c2672c4074
- a489b72510dfd07e6d05b07e8547cf25
- 9edbd2f21b81183770fd767b31c2458c
- 959e71b8f743a202eb80b65acbb60f7c
- d8508b3c7ba4f2b9ed1cf3ff28fd6b83
- 22a477da55c7391dd0fc6176241d108e
SHA-256
- 7464850d7d6891418c503d0e1732812d7703d6c1fd5cf3c821f3c202786f9422
- f3e6e8df132155daf1d428dff61f0ca53ecd02015a0a0bbe1ad237519ab3cb58
- e87177e07ab9651b48664c3d22334248e012e8a2bab02f65c93fedd79af0a74f
- 022344029b8bf951ba02b11025fe26c99193cb7c8a482c33862c9bbaa5e5528e
- 9111d458d5665b1bf463859792e950fe8d8186df9a6a3241360dc11f34d018c2
- 4bce97eff4430708299a1bb4142b9d359d8adf77a2e1673bf76485df25e6d357
- 878e3701df9b0abdaa7094e22d067c8398a9fc842cabe917fd5f75f2c84d8552
- 176e8a5a7b6737f8d3464c18a77deef778ec2b9b42b7e7eafc888aeaf2758c2d
- 48ee5d0d44a015876d867fa515b04c1998fecf19badcbd69f4f3fa8497d57215
- a4cab67569d0b35c249dc536fb25dabdc12839ed4e945c59ec826c0a241b792a
SHA1
- 1602cc32d56ab7f7d70c508696134875a0a56000
- afefb97605354c96d07d6e24a87798dd5891b583
- e9519f91c7acfe68e614fc6d3416033334b1b68c
- c91f346d077efbcf45e53e4876b6b23f1e241db4
- 2efdf82808cd7f63ebc66f553ae94127c3d7c60b
- 8380d7451f9c4477dd2e8c7c0ba46471bfc6dc27
- 60be225d1a90070d22bf2abcc740d311041cb432
- 78027c3800ff58321371a28b1e2a6d7e870add60
- 4a93fe1e7fce91f3c3d99c733d9628ed952dbf2a
- 5e38363e7c196a3627dc10a8292bb72473599c2e
URL
- https://filedn.com/lY24cv0IfefboNEIN0I9gqR
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Ensure all operating systems and software are up to date with the latest security patches.
- Employ reliable antivirus and antimalware software to detect and block known threats.
- Regularly update these tools to maintain the latest threat intelligence.
- Implement IDPS to detect and prevent unusual network activity, system behavior, or similar threats.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your accounts adds an extra layer of security and can help prevent unauthorized access even if your login credentials have been stolen.
- Regularly backing up your important data can help ensure that you don’t lose any critical information in the event of a malware infection or other data loss event.
- Be wary of emails, attachments, and links from unknown sources. Also, avoid downloading software from untrusted sources or clicking on suspicious ads or pop-ups.
- Use email filtering solutions to block malicious attachments and links that may deliver malware to users via phishing emails.
- Segment your network to limit lateral movement for attackers.
- Employ application whitelisting to only allow approved software to run on systems, reducing the risk of unauthorized applications being executed.
- Implement robust monitoring solutions to detect any unusual or suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration. Establish an effective incident response plan to respond to and mitigate any potential breaches quickly.
- Make sure all of your software, including your operating system and applications, is up-to-date with the latest security patches. This can help prevent vulnerabilities that info-stealers and other types of malware could exploit.

