Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Cybersecurity researchers have reported a surge in email phishing campaigns since early March 2024 aimed at delivering Latrodectus, a new malware loader seen as the successor to IcedID.
According to researchers, these campaigns employ oversized JavaScript files that leverage Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) to invoke msiexec.exe and install a remotely hosted MSI file via a WebDAV share. Latrodectus is designed to deploy additional payloads like QakBot, DarkGate, and PikaBot enabling various post-exploitation activities.
Latrodectus exhibits advanced capabilities including extensive enumeration and execution focus as well as a self-delete feature for running files. It disguises itself as a legitimate software library, uses source code obfuscation, and performs anti-analysis checks to evade debugging or sandbox environments.
The malware establishes persistence on Windows hosts via scheduled tasks and communicates with a command-and-control (C2) server over HTTPS to execute commands such as collecting system information, updating, restarting, and running shellcode, DLL, and executable files. Recent updates have added commands for enumerating desktop files and retrieving running process ancestry.
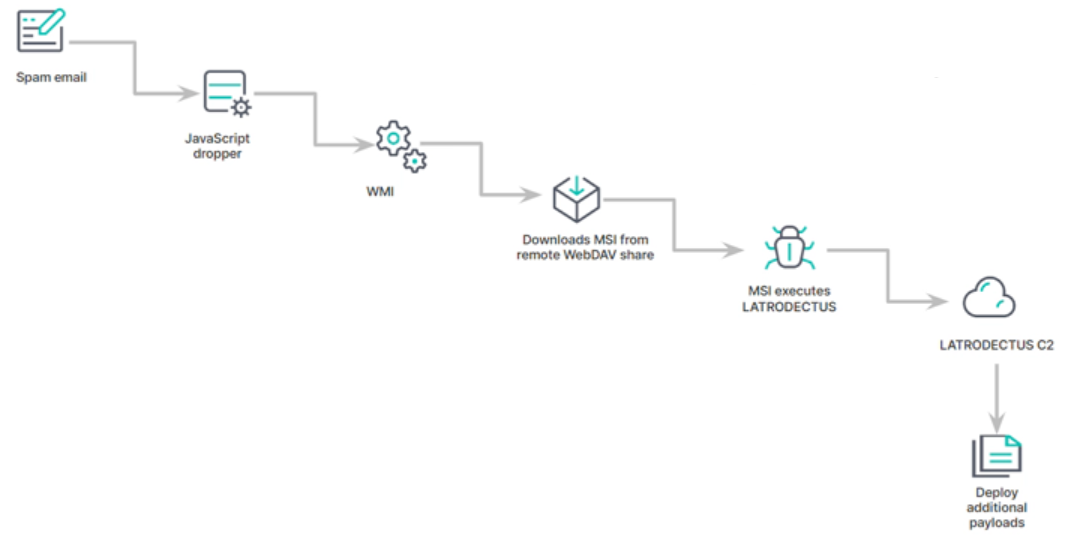
The development of Latrodectus suggests a connection with IcedID possibly indicating that Latrodectus is being developed as its replacement. Meanwhile, researchers have analyzed a phishing campaign using invoice-themed emails to deliver DarkGate malware. This campaign starts with QuickBooks-themed phishing emails that direct users to install a malicious Java archive (JAR) which executes a PowerShell script to download and launch DarkGate via an AutoIT script.
Additionally, social engineering campaigns have utilized an updated phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platform called Tycoon to harvest Microsoft 365 and Gmail session cookies, bypassing multi-factor authentication (MFA). Cybersecurity experts highlight the enhanced detection evasion capabilities of the new Tycoon version which includes obfuscation techniques and dynamic code generation to evade signature-based detection systems.
Other campaigns in March 2024 have exploited Google ads impersonating services like Calendly and Rufus to distribute the D3F@ck Loader malware. This loader, which appeared on cybercrime forums in January 2024 eventually delivers Raccoon Stealer and DanaBot. The case of D3F@ck Loader underscores the evolution of malware-as-a-service (MaaS) using Extended Validation (EV) certificates to bypass security measures.
In parallel new stealer malware families such as Fletchen Stealer, WaveStealer, zEus Stealer, and Ziraat Stealer have emerged, while the Remcos remote access trojan (RAT) has enhanced its capabilities with a PrivateLoader module. According to researchers, Remcos uses VB scripts, registry alterations, and service setups to maintain undetected infiltration and persistent control over infected systems. These developments highlight the escalating sophistication and persistence of cyber threats in 2024.
Impact
- Command Execution
- Information Theft
- Security Bypass
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- aytobusesre.com
- scifimond.com
MD5
- da8ae8e1de522b20a462239c6893613e
SHA-256
- aee22a35cbdac3f16c3ed742c0b1bfe9739a13469cf43b36fb2c63565111028c
SHA-1
- 7f65ef885815d81d220f9f42877ff0d696b0134c
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Do not download documents attached in emails from unknown sources and strictly refrain from enabling macros when the source isn’t reliable.
- Ensure that all systems, software, and applications are up-to-date with the latest security patches. Regularly check for and apply updates to eliminate known vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
- Educate employees about phishing emails, social engineering tactics, and safe online behavior. Effective training can reduce the likelihood of users inadvertently initiating an attack.
- Regularly back up critical data and systems to offline or isolated storage. Test the backup restoration process to ensure that it is effective in case of an attack.
- Deploy strong endpoint protection solutions that include advanced threat detection, behavior monitoring, and real-time protection against malware and ransomware.
- Employ robust email filtering and anti-phishing solutions to detect and prevent malicious attachments and links from reaching user inboxes.
- Conduct regular penetration testing and security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your network and systems. Address any findings promptly.
- Thoroughly assess third-party vendors and software before integrating them into your environment. Ensure they have strong security practices and adhere to cybersecurity standards.

