Severity
High
Analysis Summary
The Internet Archive has faced another significant data breach, this time involving its Zendesk email support platform. Threat actors managed to exploit exposed GitLab authentication tokens which allowed them to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data including over 800,000 support tickets dating back to 2018.
These tickets contain user requests such as removals from the Wayback Machine potentially exposing sensitive personal information. Despite repeated warnings, the Internet Archive failed to rotate its stolen tokens enabling the threat actors to exploit this vulnerability.
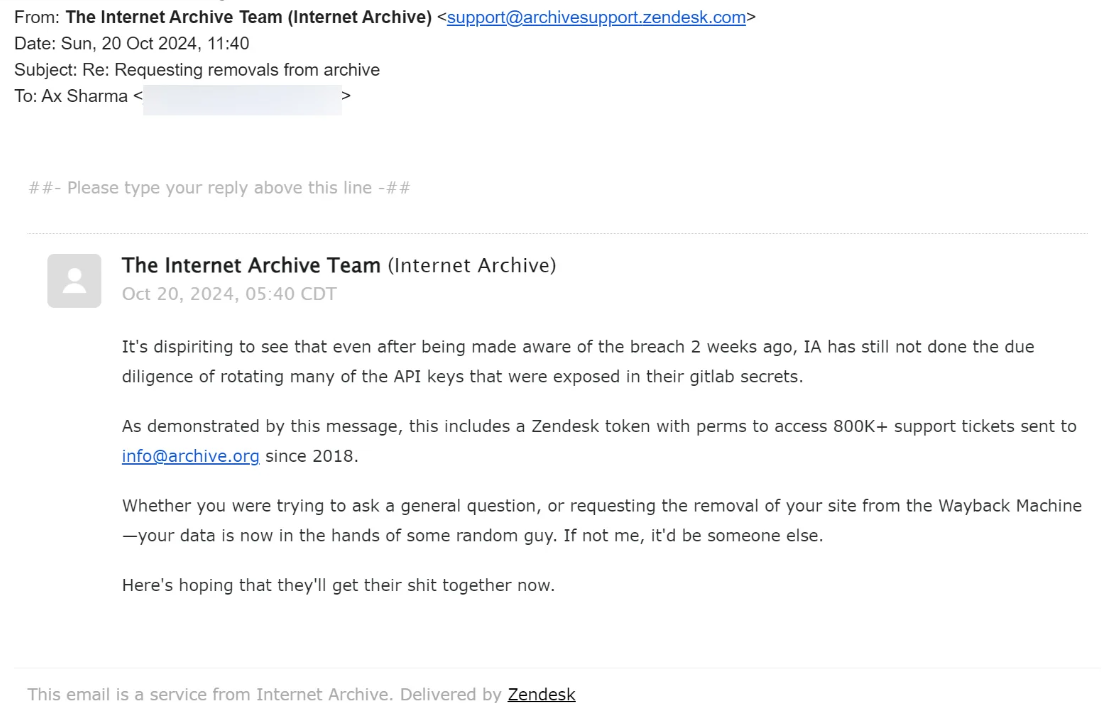
According to the threat actor, they now have access to sensitive attachments uploaded by users depending on their API access to Zendesk. If the attackers exploited this access, they could have downloaded support tickets that included personal identification documents and other sensitive information submitted by users
The breach stems from a GitLab configuration file left exposed since at least December 2022. The configuration file included authentication tokens that allowed attackers to download the organization's source code. Further investigation revealed that this code contained additional credentials, including access to the organization's database management system. As a result, the attackers claimed to have stolen 7TB of data, although they did not provide any sample data to prove their claims. The incident has raised concerns about the security of Internet Archive’s systems, especially considering the organization's slow response to prior warnings.
This breach coincided with a DDoS attack targeting the Internet Archive by a pro-Palestinian group named SN_BlackMeta, although the two attacks were unrelated. Misreporting initially blamed the breach on this group, frustrating the actual attackers. The individuals behind the data theft later contacted researchers to clarify their role and explain the breach's origins. According to the attackers, they breached the organization simply because they could, citing an exposed GitLab token as the entry point to the system.
While the breach does not appear to have been financially motivated, the Internet Archive’s popularity made it a prime target for cybercriminals seeking "street cred" within the hacker community. The stolen data is likely circulating within these circles and may eventually be leaked on dark web forums. This incident underscores the growing challenges organizations face in securing their systems, especially when sensitive authentication tokens are left vulnerable for extended periods
Impact
- Unauthorized Access
- Sensitive Data Theft
Remediation
- Regularly change passwords for all accounts and use strong, unique passwords for sensitive accounts.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all accounts to add an extra layer of security to login processes.
- Consider the use of phishing-resistant authenticators to further enhance security. These types of authenticators are designed to resist phishing attempts and provide additional protection against social engineering attacks.
- Regularly monitor network activity for any unusual behavior, as this may indicate that a cyberattack is underway.
- Organizations need to stay vigilant and follow best practices for cybersecurity to protect their systems and data from potential threats. This includes regularly updating software and implementing strong access controls and monitoring tools.
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to respond effectively in case of a security breach or data leakage.
- Maintain regular backups of critical data and systems to ensure data recovery in case of a security incident.
- Adhere to security best practices, including the principle of least privilege, and ensure that users and applications have only the necessary permissions.
- Establish a robust patch management process to ensure that security patches are evaluated, tested, and applied promptly.
- Conduct security audits and assessments to evaluate the overall security posture of your systems and networks.
- Implement network segmentation to contain and isolate potential threats to limit their impact on critical systems.
- Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.

