Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Cybercriminals are increasingly exploiting vulnerabilities in the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to gain unauthorized access to Windows systems and remotely control web browsers, posing a serious threat to enterprise networks. RDP, a Microsoft protocol used for remote system management is frequently targeted through brute-force attacks on weak credentials or by purchasing compromised access from darknet marketplaces.
According to the Researcher, Attackers often leverage tools like Nmap to scan for vulnerable systems running on the default RDP port 3389, checking for known exploits such as MS12-020. Once access is obtained, they can hijack active sessions or create new ones using credential-stealing tools like Mimikatz.
After establishing control, attackers engage in lateral movement across the network using Windows tools like PsExec and WMI to escalate privileges and compromise additional systems. A major concern is the ability to monitor and reconstruct browser activity from RDP session artifacts, including bitmap cache data stored locally on compromised machines. By using tools such as BMC-Tools, hackers can extract cached screen fragments to reveal sensitive information, including login credentials and accessed URLs. In some cases, attackers have used RDP to access private browser tabs on compromised systems, allowing them to steal sensitive data without raising immediate suspicion.
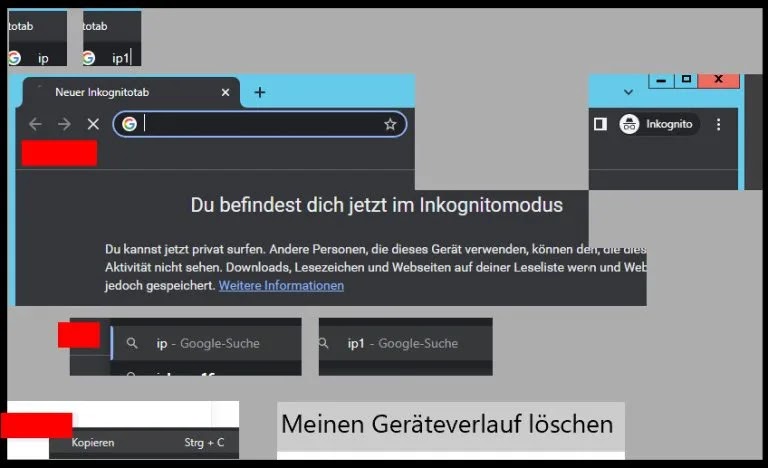
The vulnerabilities exploited in these attacks stem from multiple factors, including unpatched systems susceptible to exploits like BlueKeep (CVE-2019-0708), weak passwords that facilitate brute-force attempts, and insecure default RDP settings. Features such as persistent bitmap caching, which stores session data locally, further expose sensitive information to attackers. Additionally, attackers often deploy malicious files, such as svchost.exe, into public directories to maintain persistence and facilitate further exploitation. These weaknesses create a high-risk environment for organizations relying on remote access solutions.
To mitigate these threats, organizations must enforce strong passwords, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for RDP access, and restrict connections through firewalls or VPNs. Regular patching of systems is essential to address vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-21307, while disabling persistent bitmap caching in RDP settings reduces exposure to data leaks. Continuous monitoring of RDP activity using security solutions such as SIEM and AI-driven threat detection tools like Darktrace can help identify and mitigate suspicious behavior. Proactive security measures are crucial to safeguarding remote access protocols and preventing unauthorized access or data breaches.
Impact
- Unauthorized Access
- Sensitive Information Theft
- Privilege Escalation
- Remote Code Execution
Indicators of Compromise
CVE
- CVE-2019-0708
Affected Vendors
Microsoft
Remediation
- Regularly update Windows systems and apply security patches to mitigate known vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-21307 and BlueKeep (CVE-2019-0708).
- Use complex passwords and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for RDP access.
- Disable or limit RDP access for accounts with weak credentials.
- Allow RDP connections only through a secure VPN or firewall.
- Restrict RDP access to specific IP addresses to reduce exposure.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual RDP activity using SIEM solutions or AI-driven tools like Darktrace.
- Disable unnecessary RDP services if not required.
- Change the default RDP port (3389) to a non-standard port to reduce exposure to automated attacks.
- Disable persistent bitmap caching to prevent attackers from extracting session data.
- Enable Network Level Authentication (NLA) to require authentication before establishing an RDP session.
- Implement account lockout policies to prevent brute-force attacks.
- Use endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to identify suspicious activities.
- Regularly audit logs and RDP session activity for anomalies.

