Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Microsoft is alerting users to cyberattack operations that take advantage of trusted file hosting services—like Dropbox, OneDrive, and SharePoint—that are frequently utilized in business settings as a means of getting around security measures.
The campaigns' diverse and wide-ranging objectives enable threat actors to carry out business email compromise (BEC) attacks, compromise identities and devices, and eventually cause financial fraud, data exfiltration, and lateral movement to other endpoints. An increasingly common risk vector used by adversaries to blend in with legitimate network traffic is the weaponization of legitimate internet services (LIS). This allows adversaries to often get by standard security measures and makes attribution attempts more difficult.
The strategy is sometimes called living-off-trusted sites (LOTS), as it utilizes the confidence and familiarity of these services to sidestep email security guardrails and transmit malware. Since mid-April 2024, Microsoft says to have seen a new trend in phishing attacks that leverage reputable file-hosting sites and involve files with view-only and restricted access.
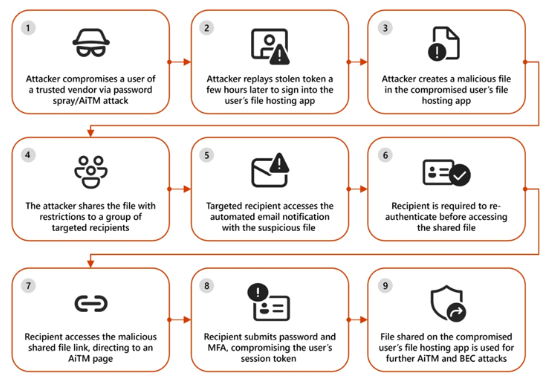
These kinds of attacks usually start with a user within a reliable vendor being compromised. This allows the attackers to stage malicious files and payloads on the file hosting service, which they can then share with a target organization. The files that are delivered via phishing emails are set up so that only the intended recipient can access them. To proceed, the recipient must either re-authenticate by providing their email address and a one-time password (OTP) that they received through a notification service, or they must be logged in to the file-sharing service, such as Dropbox, OneDrive, or SharePoint.
What's more, the files sent as part of the phishing attempts are put in "view-only" mode, blocking the ability to download and identify embedded URLs within the file. When a recipient tries to access the shared file, they are then asked to confirm their identity by sending a one-time password to their email address and supplying their email address.
The target is directed to click on another link to access the actual contents after they have been successfully authenticated. But in the process, it sends users to a phishing page run by an adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) that takes their two-factor authentication (2FA) tokens and password. This gives the threat actors the ability to take over the account and utilize it to carry out other frauds and scams, such as financial fraud and BEC attacks. Despite being generic and opportunistic, these campaigns use advanced tactics to carry out social engineering, avoid detection, and extend the threat actor's reach to more accounts and renters.
Impact
- Security Bypass
- Identity Theft
- Financial Loss
- Data Exfiltration
Remediation
- Ensure all operating systems and software are up to date with the latest security patches.
- Employ reliable antivirus and antimalware software to detect and block known threats.
- Regularly update these tools to maintain the latest threat intelligence.
- Implement IDPS to detect and prevent unusual network activity, system behavior, or similar threats.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your accounts adds an extra layer of security and can help prevent unauthorized access even if your login credentials have been stolen.
- Regularly backing up your important data can help ensure that you don’t lose any critical information in the event of a malware infection or other data loss event.
- Be wary of emails, attachments, and links from unknown sources. Also, avoid downloading software from untrusted sources or clicking on suspicious ads or pop-ups.
- Use email filtering solutions to block malicious attachments and links that may deliver malware to users via phishing emails.
- Segment your network to limit lateral movement for attackers.
- Employ application whitelisting only to allow approved software to run on systems, reducing the risk of executing unauthorized applications.
- Implement robust monitoring solutions to detect any unusual or suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration. Establish an effective incident response plan to respond to and mitigate any potential breaches quickly.
- Make sure all of your software, including your operating system and applications, is up-to-date with the latest security patches. This can help prevent vulnerabilities that info-stealers and other types of malware could exploit.

