Severity
High
Analysis Summary
A new timing-based vulnerability, dubbed "DoubleClickjacking," has been uncovered by security researchers. This sophisticated clickjacking variant leverages a double-click sequence to bypass established security measures including X-Frame-Options headers and SameSite cookies. Unlike traditional clickjacking, where a single click initiates malicious actions, DoubleClickjacking exploits the gap between two clicks to manipulate user interactions. This method enables attackers to hijack accounts and conduct unauthorized actions on nearly all major websites with the potential for widespread exploitation.
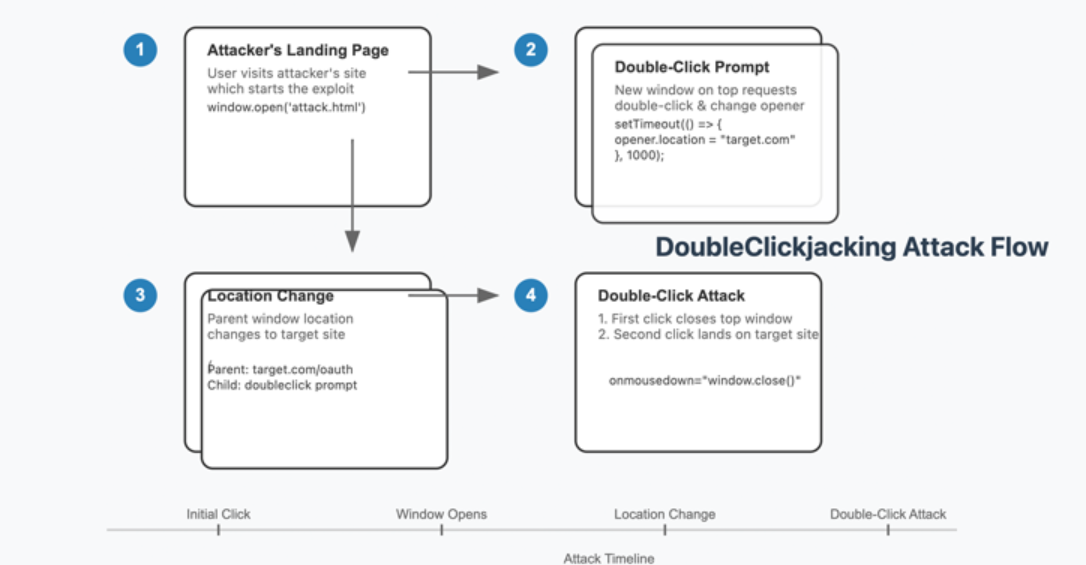
According to the researchers, a user visits a malicious site which opens a new browser window or tab often under the guise of a harmless prompt like a CAPTCHA verification. The new window requests a double-click action and during this interaction, the parent site uses JavaScript to redirect the user to a malicious page. Simultaneously, the top window closes tricking users into unknowingly granting permissions such as approving a malicious OAuth application. This seamless manipulation of UI elements during the brief interval between clicks allows attackers to bypass traditional defenses and compromise accounts with minimal user interaction.
The primary challenge lies in the inability of current security measures to counteract this novel attack. Existing solutions such as X-Frame-Options SameSite cookies, and Content Security Policies (CSPs) are ineffective against DoubleClickjacking as they were not designed to mitigate double-click event exploitation. This vulnerability emphasizes the need for enhanced browser standards and proactive security measures. Researchers recommend client-side defenses such as disabling critical buttons until a verified mouse gesture or keypress is detected an approach already adopted by some services like Dropbox.
DoubleClickjacking represents an evolution in UI-based attacks, highlighting the ingenuity of adversaries in exploiting overlooked gaps in event timing. It also draws attention to related threats such as cross-window forgery (gesture-jacking) which persuades users to press or hold keys to trigger malicious actions. Both vulnerabilities underscore the urgency for website owners and browser vendors to adopt advanced security mechanisms. Long-term solutions may include new browser standards that specifically address timing-based UI manipulation. This discovery serves as a wake-up call for the cybersecurity community to reevaluate and fortify defenses against increasingly complex attack vectors.
Impact
- Unauthorized Access
- Sensitive Data Theft
- Financial Loss
Remediation
- Ensure buttons requiring user interaction (like "Approve" or "Submit") are disabled until a genuine user action (e.g., mouse movement or key press) is detected.
- Add a delay or validation between clicks to prevent automated or rapid consecutive actions.
- Prevent predictable button IDs or UI structures to make it harder for attackers to manipulate them.
- Verify critical actions on the client side to detect and block suspicious interactions.
- Combine Content Security Policy (CSP) with frame-ancestor restrictions to limit unauthorized frames or pop-ups.
- Introduce browser-level protections specifically targeting double-click exploits, similar to X-Frame-Options but tailored for timing-based attacks.
- Implement stricter checks on newly opened windows or tabs that require user interaction.
- Detect and block malicious attempts to swap out UI elements between clicks.
- Be cautious of websites that open unexpected pop-ups or request double-click actions.
- Keep your browser updated to benefit from the latest security patches and protections.
- Log out of critical accounts (like banking or email)
- Use Browser Extensions: Consider security extensions that block unauthorized scripts or prevent malicious redirections.
- Regularly analyze user behavior to detect anomalies and mitigate potential attacks.
- Raise awareness about the risks of clicking on suspicious prompts or pop-ups.
- Perform regular penetration tests to identify and fix timing-based attack surfaces.

