Severity
High
Analysis Summary
A previously unknown feature of ClickFix-style attacks that rely on exploiting a single ad network service as part of a malvertising-driven information theft operation called DeceptionAds has been uncovered by cybersecurity researchers.
Through a network of more than 3,000 content sites that funnel traffic, this campaign, which is solely dependent on one ad network for propagation, exemplifies the fundamental mechanisms of malvertising by delivering over 1 million daily 'ad impressions' in the last ten days and causing thousands of victims to lose their accounts and money every day.
According to recent reports from several cybersecurity firms, the campaigns entail sending users to fake CAPTCHA verification pages from websites that sell pirated movies and other websites, instructing them to copy and run a Base64-encoded PowerShell command. This ultimately results in the deployment of information stealers such as Lumma. Researchers have reported that several "unattributed" threat clusters have adopted the same social engineering technique to distribute remote access trojans, stealers, and even post-exploitation frameworks like Brute Ratel C4, demonstrating that the attacks are no longer limited to a single actor.
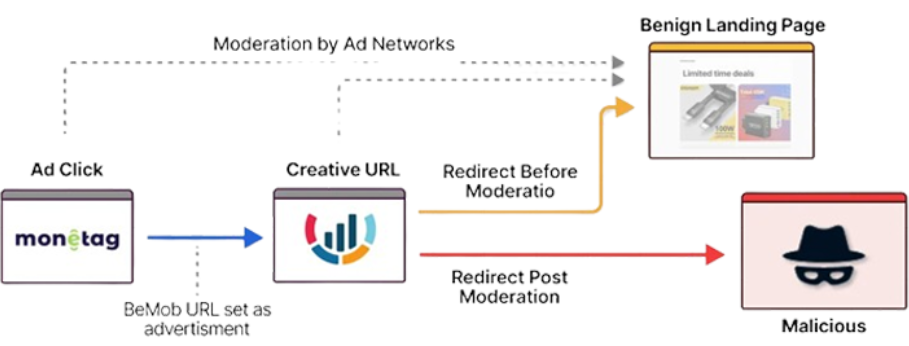
The campaign's beginnings, according to researchers, may be traced back to Monetag, a platform that purports to provide a variety of ad formats to monetize websites, social traffic, and Telegram Mini Apps. Threat actors also use platforms like BeMob ad-tracking to conceal their malicious intent. After website owners (i.e., threat actors) register with Monetag, traffic is sent to a Traffic Distribution System (TDS) run by the malvertising ad network, which finally directs users to the CAPTCHA verification page. This is essentially how the campaign works.
The attackers took advantage of BeMob's reputation by providing Monetag's ad management system with a benign BeMob URL rather than the actual phony captcha page, making Monetag's content moderation efforts more difficult. The fraudulent CAPTCHA website, which is hosted on services like Oracle Cloud, Scaleway, Bunny CDN, EXOScale, and even Cloudflare's R2, is ultimately redirected by this BeMob TDS. As of late November 2024, Monetag has deleted more than 200 accounts associated with the threat actor after responsible disclosure. In an attempt to do the same, BeMob deleted the cloaking accounts. However, as of December 5, there are indications that the campaign has resumed.
The results emphasize the necessity of strict account validation and content control to stop fraudulent registrations. This campaign demonstrates how ad networks, which are intended for lawful purposes, can be used maliciously, from cloaking tactics and complicated redirect chains to misleading publisher websites that offer pirated or clickbait content. Ad networks, publishers, ad statistics services, and hosting providers all have a part to play but frequently evade accountability, leading to a disjointed chain of duties.
Impact
- Sensitive Data Theft
- Unauthorized Access
- Financial Loss
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- cdn-downloads-now.xyz
URL
- http://ajmaboxanherulv1.b-cdn.net/JSKADull.html
- http://anti-automation-v2.b-cdn.net/verf-v2.html
- http://bmy7etxgksxo.objectstorage.sa-santiago-1.oci.customer-oci.com/n/bmy7etxgksxo/b/
- http://bot-systemexplorer.b-cdn.net/recaptcha-v4-protocol-nov23.html
- http://check-cf-ver1.b-cdn.net/version3/cf-check.html
- http://dedicloadpgeing.b-cdn.net/dedicated-captcha-page.html
- http://encryption-code-verification.b-cdn.net/recaptcha-verification.html
- http://file-typ-botcheck-v1.b-cdn.net/prove-human-recaptcha.html
- http://izmncdnboxuse01.b-cdn.net/final-step-to-continue.html
- http://newverifyyourself-system1.b-cdn.net/recaptcha_verification-new.html
- http://objectstorage.ap-mumbai-1.oraclecloud.com/n/bmy7etxgksxo/b/bucket-aws-vip/o/
- http://precious-valkyrie-cea580.netlify.app/recaptcha-sep-v2-1-baba.html
- http://sys-update-botcheck.b-cdn.net/get-this-puzzle-solved.html
- http://upgraded-botcheck-encryption.b-cdn.net/verify-human-recaptcha.html
- http://verifyyourself-system.b-cdn.net/recaptcha_verification-new.html
- http://weoidnet09.b-cdn.net/IQWJDolx.html
- http://marimarbahamas.me/downloads/index.html
- https://addonclicks.com/go/aa22d074-412b-41b9-ba13-7dcf967019d9
- https://yourtruelover.com/go/d05741b5-5782-4882-b0d0-d5cbf5c14f58
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Ensure that all operating systems, software, and applications are regularly updated with the latest security patches.
- Conduct regular security awareness training for users to recognize and avoid phishing emails.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions promptly. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets.
- Along with network and system hardening, code hardening should be implemented within the organization so that their websites and software are secure. Use testing tools to detect any vulnerabilities in the deployed codes.
- Implement network segmentation to limit lateral movement within the network.
- Implement continuous monitoring of network traffic and endpoint activities to detect any unusual or suspicious behavior.
- Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective response in case of a security incident.
- Implement SIEM solutions to centralize log collection and analysis. This can help in identifying patterns of suspicious behavior and provide timely alerts for potential security incidents.
- Regularly back up critical data and ensure that the backup copies are stored securely.

