Severity
High
Analysis Summary
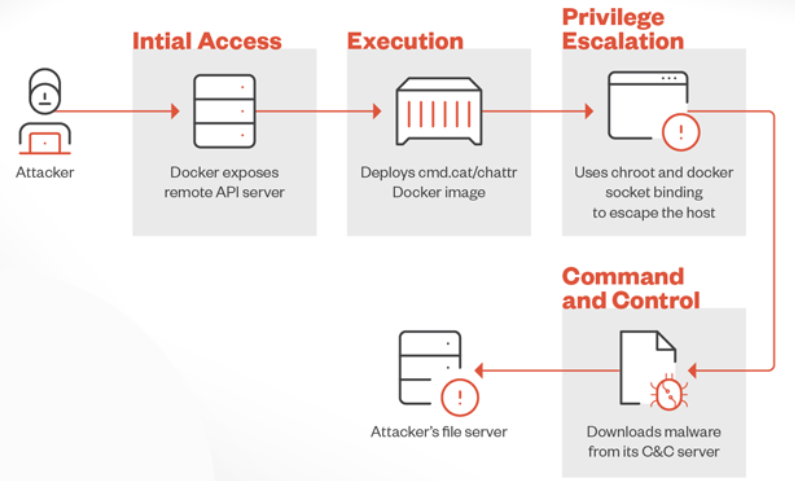
An ongoing cryptojacking campaign that uses less secured Docker instances to deploy cryptocurrency miners for profit has been connected to the threat actor Commando Cat. The payload is retrieved by the attackers using their command-and-control (C&C) infrastructure through the use of the cmd.cat/chattr docker image container.
Initially reported by researchers earlier this year, Commando Cat gets its name from the fact that it creates a benign container using the open-source Commando project. Targeting improperly configured Docker remote API servers allows the attacks to launch a Docker image called cmd.cat/chattr, which is subsequently used as a foundation to create a container, utilize the chroot command to escape its limits, and access the host OS system.
The last step is running a shell script to retrieve the malicious miner binary from a C&C server using the curl or wget commands. ZiggyStarTux, an open-source IRC bot built on the Kaiten (also known as Tsunami) malware, is thought to be binary. This attack campaign is noteworthy because it uses Docker images to install cryptojacking scripts on computers that have been compromised. By using this strategy, attackers can take advantage of security flaws in Docker setups and avoid being discovered by security tools.
The disclosure coincides with a revelation that a suspected Chinese-speaking threat actor is using long-standing security flaws in ThinkPHP applications (such as CVE-2018-20062 and CVE-2019-9082) to deliver a web shell known as Dama as part of a campaign that began on October 17, 2023. To establish a first footing, the exploit tries to obtain more obfuscated code from another compromised ThinkPHP server. Once the system has been successfully exploited, the attackers will install Dama, a Chinese-language web shell, to continue having persistent access to the server.
Advanced features of the web shell include the ability to collect system information, upload files, scan network ports, elevate privileges, and navigate the file system, which allows threat actors to obfuscate their activities by performing actions like file deletion, editing, and timestamp modification. The latest attacks, which were started by a Chinese-speaking opponent, show that attackers are increasingly employing fully functional web shells intended for sophisticated victim control. It's interesting to note that not every targeted customer used ThinkPHP, indicating that the attackers might be targeting a variety of systems randomly.
Impact
- Cryptocurrency Theft
- Financial Loss
- Security Bypass
- Sensitive Information Theft
Indicators of Compromise
IP
- 45.9.148.193
- 80.239.140.66
MD5
- 37a193112bd3af6c71f7e98837dbfb3f
SHA-256
- 9c7a12678651d72127c3c6e4dac250439fa4a3be0a8728754cea327c86a529a2
SHA1
- 253937627e0729ca2cb81b286c8f35d7421417b3
URL
- http://leetdbs.anondns.net/z
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Ensure all operating systems and software are up to date with the latest security patches.
- Employ reliable antivirus and antimalware software to detect and block known threats.
- Regularly update these tools to maintain the latest threat intelligence.
- Implement IDPS to detect and prevent unusual network activity, system behavior, or similar threats.
- Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) on your accounts adds an extra layer of security and can help prevent unauthorized access even if your login credentials have been stolen.
- Regularly backing up your important data can help ensure that you don’t lose any critical information in the event of a malware infection or other data loss event.
- Be wary of emails, attachments, and links from unknown sources. Also, avoid downloading software from untrusted sources or clicking on suspicious ads or pop-ups.
- Use email filtering solutions to block malicious attachments and links that may deliver malware to users via phishing emails.
- Segment your network to limit lateral movement for attackers.
- Employ application whitelisting to only allow approved software to run on systems, reducing the risk of unauthorized applications being executed.
- Implement robust monitoring solutions to detect any unusual or suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration. Establish an effective incident response plan to quickly respond to and mitigate any potential breaches.
- Make sure all of your software, including your operating system and applications, is up-to-date with the latest security patches. This can help prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited by info-stealers and other types of malware.

