Severity
High
Analysis Summary
A novel tool dubbed ‘MrAgent’ has been developed by the RansomHouse ransomware gang to help in automating the distribution of its data encryptor targeting several VMware ESXi hypervisors.
RansomHouse is a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation that was first discovered in December 2021 and uses double extortion tactics. The operation also set up a dedicated victim extortion page on the dark web in May 2022. The RansomHouse gang has not been too active like the other infamous groups such as LockBit, Play, Clop, and ALPHV/BlackCat but the researchers stated that it targeted multiple large-sized organizations within the previous year.
It is not uncommon for ransomware groups to target ESXi servers because they deploy virtual environments that usually contain valuable data that can be stolen and used for extortion. ESXi servers also usually have critical applications and services running for businesses, like email servers and databases, so a ransomware attack can easily disrupt operations.
Security analysts discovered a new binary that was used in RansomHouse attacks that seems to have been specifically developed for automating the gang’s attacks on ESXi systems. This sample was first reported in September 2023. The main function of MrAgent is to identify the targeted system, turn off its firewall, and finally automate the ransomware deployment process across various hypervisors at the same time to compromise all the managed virtual machines. The tool also supports custom configurations to deploy ransomware that can be retrieved directly from the command-and-control (C2) server. These configurations include setting up the encryptor command and its arguments, applying passwords on the hypervisor, changing the welcome message to a ransom note that is displayed on the hypervisor’s monitor, and scheduling an encryption event.
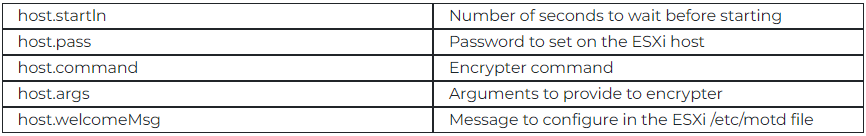
MrAgent is also capable of executing local commands on the hypervisor that are received from the C2 for deleting files, dropping active SSH sessions to prevent any interference during the encryption process, and sending back information about the currently running virtual machines. The reason for disabling firewalls and dropping non-root SSH sessions is to be able to minimize the chances of detection by administrators and easily flying under the radar, hence increasing the success rate and impact of the attack by targeting all reachable virtual machines simultaneously.
The researchers stated, “The efforts to (further) automate the steps that are otherwise often executed manually shows both the interest and willingness of the attacking affiliate to target large networks.”
There is also a Windows version of MrAgent that has been spotted by the researchers and shows similar core functionality while also featuring OS-specific adaptations like using PowerShell for carrying out certain tasks. This shows that RansomHouse intends to extend the tool’s applicability to maximize the impact of their campaigns especially when their target is both a Windows and Linux user.
The security concerns raised by tools such as MrAgent are very severe, so it is advised that organizations should implement robust and comprehensive security measures, like updating software promptly, regularly monitoring the network, and implementing strong access controls to defend against these kinds of threats.
Impact
- Sensitive Information Theft
- Data Exfiltration
- Financial Loss
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- d2853c1d92c73dc047cdb1f201900a99
- ef46880a8583da64cebea1e8f8cb1fb3
- e79984ea02b2049b1e74452013529da5
- 6f53f99b0a19150d53244d691dd04e80
- 446237df80b3f155519b5fde00a82087
- e56c97cb4f9df25845cda36e3cd7d597
- dd2fee6e1ace30b2d3be7b45f2fd6a82
- 0dcbb7c7af77efd4a2b39f2303806fcd
SHA-256
- 8189c708706eb7302d7598aeee8cd6bdb048bf1a6dbe29c59e50f0a39fd53973
- bfc9b956818efe008c2dbf621244b6dc3de8319e89b9fa83c9e412ce70f82f2c
- 3934b3da6bad0b4a28483e25e7bab919d7ed31f2f51cca22c56535b9f8183a0e
- afe398e95a75beb4b0508c1bbf7268e8607d03776af0b68386d1e2058b374501
- 2c1a4fe4a2ac4f0a49052f9521458136eb477fe23665dc4b7076fbd32de3005d
- 2c1475f1b49a8b93a6c6217be078392925535e084048bf04241e57a711f0f58e
- 0a77e537c64336f97a04020e59d17d09d459d1626a075878e2b796d1e1033038
- d36afcfe1ae2c3e6669878e6f9310a04fb6c8af525d17c4ffa8b510459d7dd4d
SHA-1
- 5b1541ee4ccfc020a081361ea8d6fe48d20e602a
- 51cfd3290e562367bc5b0930eb5ad70586979b75
- 6bb0c60195d90b032a3488b50a38a797dfcf9104
- d6d6174ec5370d8ffa8a163863544d52501813dc
- 23f83a96144ace88b0491ab519ead733342da0e6
- 048b3942c715c6bff15c94cdc0bb4414dbab9e07
- b348b50aa1868140d750f633d4bd7c8cebc86f1c
- 0a18d66e3f72e21b9a507739dbeb009d017dcfe0
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Maintain Offline Backups – In a ransomware attack, the adversary will often delete or encrypt backups if they have access to them. That’s why it’s important to keep offline (preferably off-site), encrypted backups of data and test them regularly.
- Patch and upgrade any platforms and software timely and make it into a standard security policy. Prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities and zero-days.
- Emails from unknown senders should always be treated with caution. Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions promptly. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets.
- Conduct a thorough assessment to determine the extent of the ransomware attack. Identify the systems, files, and data that have been compromised or encrypted by the ransomware.
- If reliable and unaffected backups are available, ensure they are secure and intact. Disconnect any compromised backup systems to prevent further encryption. Restore data and systems from clean backups once the affected systems have been cleaned and secured.
- Restrict user privileges and implement the principle of least privilege. Users should only have access to the systems and files necessary for their roles, reducing the potential impact of ransomware attacks.

