Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Cybercriminals have adopted an innovative code distribution method known as ‘EtherHiding,’ exploiting Binance’s Smart Chain (BSC) contracts to conceal malicious scripts within the blockchain. This campaign was discovered about two months ago. It is the latest iteration of an ongoing malware campaign that uses infected WordPress sites to issue a fake warning page to the visitors that urges them to update their browsers in order to access the websites, which leads to the deployment of information stealer malware like Lumma, Amadey, and RedLine.
“While their initial method of hosting code on abused Cloudflare Worker hosts was taken down, they’ve quickly pivoted to take advantage of the decentralized, anonymous, and public nature of blockchain,” said the security researchers.
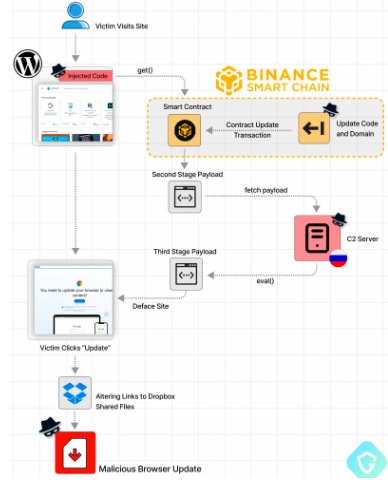
The WordPress sites are being targeted by the threat actors using publicly disclosed security vulnerabilities in plugins and utilizing their own malicious plugins in order to breach those websites.
EtherHiding represents a recent method employed by threat actors, referred to as ‘ClearFake,’ for disseminating injected code within compromised websites, enabling the display of deceptive browser update overlays.
By observing the latest attacks, the researchers found out that the compromised sites are injected with hidden JavaScript that creates a smart contract with an attacker-controlled blockchain address to query the BNB Smart Chain. Its goal is to fetch a second-stage script which then receives a third-stage payload from the actor’s C2 server to display the fake update messages on the browser. When the unsuspecting visitor clicks on the update button, they are redirected to a Dropbox or other legitimate file hosting link to download a malicious executable file.
“As this is not an address used in any financial or other activity that victims can be lured to transfer funds or any other kind of Intellectual property to — visitors of compromised WordPress sites have no clue as to what is going on under the hood,” the researchers explained further.
These attack chains have been observed by researchers to lead to the deployment of malware loader such as HijackLoader and IDAT Loader. These are responsible for the installation of several trojans and stealers like Lumma, DanaBot, Raccoon, Remcos, RedLine, Vidar, and SystemBC.
Plugins are increasingly becoming an attack surface for WordPress, which urges the need to adhere to the best security practices for users relying on the content management system. Keeping systems up-to-date with the latest patches and enforcing strong passwords helps a lot in keeping the risk minimum.
Emerging as an evolution of ClearFake campaigns, EtherHiding exemplifies the ongoing evolution of tactics employed by threat actors to enhance the resilience of their attacks against takedowns. Should this approach prove effective, blockchain abuse may become a fundamental component of numerous payload delivery attack sequences in the forthcoming months.
Impact
- Code Injection
- Sensitive Data Theft
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- 921hapudyqwdvy.com
- 98ygdjhdvuhj.com
- boiibzqmk12j.com
- bookchrono8273.com
- bpjoieohzmhegwegmmuew.online
- cczqyvuy812jdy.com
- indogevro22tevra.com
- ioiubby73b1n.com
- kjniuby621edoo.com
- lminoeubybyvq.com
- nbvyrxry216vy.com
- nmbvcxzasedrt.com
- oekofkkfkoeefkefbnhgtrq.space
- oiouhvtybh291.com
- oiuugyfytvgb22h.com
- oiuytyfvq621mb.org
- ojhggnfbcy62.com
- opkfijuifbuyynyny.com
- pklkknj89bygvczvi.com
- poqwjoemqzmemzgqegzqzf.online
- pwwqkppwqkezqer.site
- reedx51mut.com
- sioaiuhsdguywqgyuhuiqw.org
- ug62r67uiijo2.com
- vcrwtttywuuidqioppn1.com
- vvooowkdqddcqcqcdqggggl.site
- ytntf5hvtn2vgcxxq.com
- zasexdrc13ftvg.com
- ziucsugcbfyfbyccbasy.com
IP
- 109.248.206.49
MD5
- bec0c1cd56a658c355692f3d0131598f
- 8c7f9e2e1533bee0c53f494aa84b0d3d
- 5d9e72d1e3a99bec71fad561fa95037c
- f1c9c05e648e58b6bef8dada7654a88e
- 1cab41fd402c7e2060117dccff8926a3
- 5225371f32a1ba8a5daa8f14ce64e8bf
- de2456b94b4d4019ad591379205ebd6e
- a655b9c347ce862da682883508be4880
- c5fd555dbe14fe81441d7ef3699a6b77
- 3a198a130c1d6eef33fc52d39d83347b
- a3fec32282873b302adaeef78c085aee
SHA-256
- d0c56875fb19a407a86292e35dffec6caabbdbf630fbb79de4eec04708fa7b66
- 37bba90d20e429ce3fd56847e4e7aaf83c62fdd70a7dbdcd35b6f2569d47d533
- b029b40badab029cbd916ab2e5147e9f01abd147e1bf9e5ed1564ee44a0d087f
- 1a99ac759fcd881729b76c2904476b4201e794df2d0547c954ea37be7c153131
- 633124ed8d7af6dd22722ee43abfe9b0ad97798a1d48b951abdc1ad88e83c702
- 1743f4a392b6d2ad0d47a7a57e277e1a29ecf459275b604919a6131739afdaad
- 788567d3cc693dd5d0dada9f4e1421755c1d74257544ba12b502f085a620585e
- 3d77b34ba6dbb49d594e2be590a87f682e1875d2565ff18bdeafc66c9d5594ea
- 80f05865e59ec4e12e504adbf5fae3d706b5d27e5ab2fc52fcd0feb19365c7b0
- e041b3eaaed1c0ad37e7f91717ee5b0e12e922b67bbe1e69a4c68c80baf22b4f
- 8ba53b5d773bc157df65fb0941c24e1edbc7c7b47e37b3f7a01751fc3b1a701a
SHA-1
- f703382e7504fe8a3f10aecafe7fb9380df17ecc
- 718f0861dfbd06cbac887a6aa9f912797d3aaa78
- fbc94c649ba3d8bb6c7e1d98e7fdeea40cd395b2
- 51e14be2940ae38c6428bf33bb8a9a08ae36ec69
- 0c88c470dc7ecbccdc3aaa915be08f5f23dca190
- 8f9221f0fd7c5cfe50f12337b5ce35f4c07c6e3e
- 7f98a888fb52ed5627d7b374439ca14616f68d33
- fd3e63a78fd4724600b9429edc605cebf90a5947
- 7020c067e90e5523a69963a1514d4588ede36cde
- 6c92b9730ed0d7b43e0fb6f9bf5bf47aa0fd7cff
- df5c2d7162265c4080d88b47eb0aa2f42e398570
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls
- Ensure that all systems, software, and applications are up-to-date with the latest security patches. Regularly check for and apply updates to eliminate known vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
- Educate employees about phishing emails, social engineering tactics, and safe online behavior. Effective training can reduce the likelihood of users inadvertently initiating an attack.
- Regularly back up critical data and systems to offline or isolated storage. Test the backup restoration process to ensure that it is effective in case of an attack.
- Use strong, unique passwords for your WordPress admin accounts. This includes both the admin user and any other accounts with elevated privileges.
- Delete any user accounts that don’t need administrative privileges.
- Maintain regular backups of your website’s content and database.
- Implement a web application firewall to filter out malicious traffic and protect against common web-based threats.
- Implement strong access controls, including limiting login attempts and using two-factor authentication (2FA) to enhance login security.
- Deploy strong endpoint protection solutions that include advanced threat detection, behavior monitoring, and real-time protection against malware and ransomware.
- Employ robust email filtering and anti-phishing solutions to detect and prevent malicious attachments and links from reaching user inboxes.
- Conduct regular penetration testing and security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your network and systems. Address any findings promptly.
- Thoroughly assess third-party vendors and software before integrating them into your environment. Ensure they have strong security practices and adhere to cybersecurity standards.


