Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Cybercriminals are leveraging YouTube videos that feature content related to cracked applications to lure users into downloading an info-stealer malware named Lumma. These YouTube videos usually show content related to pirated software, like installation guides, and use malicious URLs that are usually shortened using services such as TinyURL.
This is not the first time that threat actors have used cracked software video on YouTube to propagate stealer malware as similar attack chains have been observed in the past that delivered clippers, stealers, and crypto miner malware. This way, attackers can utilize compromised devices to commit information and cryptocurrency theft and abuse the resource for illicit mining.
The latest attack sequence analyzed by researchers shows that users who are searching for pirated versions of legitimate video editing software on YouTube are prompted to visit a link that is in the video’s description, which redirects the victim to a malicious installer posing as the legitimate software hosted on MediaFire.
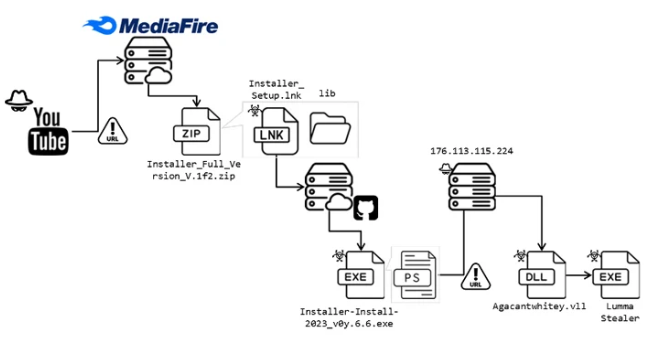
The ZIP file carries a Windows shortcut (LNK) pretending to be the setup file that downloads a .NET loader hosted on a GitHub repository. It then loads the Lumma stealer payload after carrying out a series of checks to determine if it is being run in a virtual environment as well as for anti-debugging. Lumma Stealer is written in C language and has been offered for sale as malware-as-a-service on dark web forums since at least 2022. It can steal and exfiltrate sensitive data to an actor-controlled server.
The development comes after researchers warned of stream-jacking attacks on YouTube where cybercriminals hijack high-profile accounts using phishing attacks deploying the RedLine Stealer malware to steal their session cookies and credentials to promote crypto scams. It also follows the revelation of an AsyncRAT campaign going on for at least 11 months that uses phishing lures to download a hidden JavaScript file that drops the remote access trojan.
Impact
- Cryptocurrency Theft
- Credential Theft
- Unauthorized Access
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- 757661287c20b63b1c6ae4f66fc0c6d8
- 6d07e04a6926d1dd6cc7805f866114a4
SHA-256
- 483672a00ea676236ea423c91d576542dc572be864a4162df031faf35897a532
- 01a23f8f59455eb97f55086c21be934e6e5db07e64acb6e63c8d358b763dab4f
SHA-1
- c22bbfca22798c9505e311bc1fcc417b8f7ae272
- 55dd745220a09fe110ed6f92fc883b566ba7f47a
Domain Name
- netovrema.pw
- opposesicknessopw.pw
- politefrightenpowoa.pw
- chincenterblandwka.pw
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Do not download documents attached in emails from unknown sources and strictly refrain from enabling macros when the source isn’t reliable.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions on time. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets.
- Along with network and system hardening, code hardening should be implemented within the organization so that their websites and software are secure. Use testing tools to detect any vulnerabilities in the deployed codes.
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Patch and upgrade any platforms and software timely and make it into a standard security policy. Prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities and zero-days.
- Develop and regularly update an incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in case of a security breach. Test the plan through simulations to ensure its effectiveness.

