Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Chaos is a customizable ransomware builder that emerged on June 9, 2021 (in underground forums) by falsely marketing itself as the .NET version of Ryuk despite sharing no such overlaps with the notorious counterpart. Since then, it has undergone active development and quick advancements, which have persuaded several attacker groups to adopt it. The most recent version, Yashma, was observed in the wild in May 2022. Yashma allows attackers to configure the ransomware so that it does not execute depending on the language chosen on the victim's device. It can also disable antivirus software, backup, storage, remote desktop, and credential vault services on victims' machines. Malware developers frequently employ this strategy to avoid infecting computers in their region, which would draw the attention of local law authorities. The Chaos ransomware generator is said to lack still some of the capabilities that are seen in many existing ransomware families.
Chaos Ransomware is a serious threat to individuals and organizations, as it can result in the loss of valuable data and disruption to normal business operations. To protect against Chaos Ransomware and other similar threats, it is recommended that individuals and organizations implement a robust cybersecurity program, including regular software updates, anti-malware protection, and employee training on the dangers of phishing and social engineering.
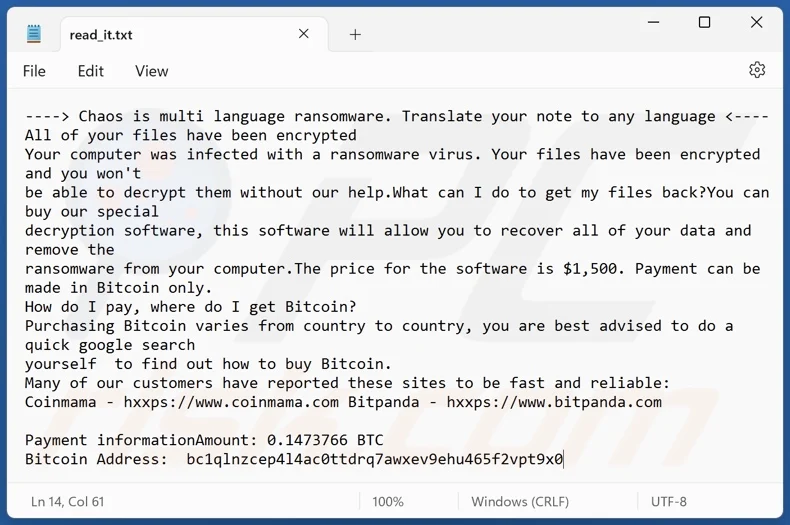
Impact
- File Encryption
- Financial Loss
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
5d2423ef31627e3095afee9f11230c8e
86eaf6459bb8f3da5e0f8c20eb4fcd9d
SHA-256
b032335922778ce4091c5f11f9906e479b82d7b02aecc6b268a45ce7b0d14fcd
31e1948d4e15f5eebeeb8c43d57ae0398b39d0edea908df6bcd6e032bbdb93e5
SHA1
dae7f2987a406e2cb496e38cfb7995fce091e565
6f39725318a0787ee1d2a7f56e6d7b534108ec44
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Maintain Offline Backups - In a ransomware attack, the adversary will often delete or encrypt backups if they have access to them. That’s why it’s important to keep offline (preferably off-site), encrypted backups of data and test them regularly.
- Emails from unknown senders should always be treated with caution.
- Never trust or open " links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.

