Severity
High
Analysis Summary
As part of a cyber-espionage campaign aimed at the United Arab Emirates and the wider Gulf area, the Iranian threat actor known as OilRig has been seen leveraging a privilege escalation vulnerability affecting the Windows Kernel that has since been patched.
The APT uses advanced strategies, such as installing a backdoor that uses Microsoft Exchange servers to steal credentials and using flaws like CVE-2024-30088 to escalate privileges. Under the alias Earth Simnavaz—also known as APT34, Crambus, Cobalt Gypsy, GreenBug, Hazel Sandstorm (formerly EUROPIUM), and Helix Kitten—the cybersecurity firm is keeping tabs on the threat actor.
The attack chains involve the introduction of recently discovered vulnerabilities into the adversary's exploit arsenal and deploying an as-yet-undocumented implant that can exfiltrate credentials through on-premises Microsoft Exchange servers, a tried-and-true strategy. Microsoft addressed CVE-2024-30088 in June 2024. It is related to a Windows kernel privilege escalation vulnerability that, if successful, might be used to elevate an attacker's privileges to SYSTEM.
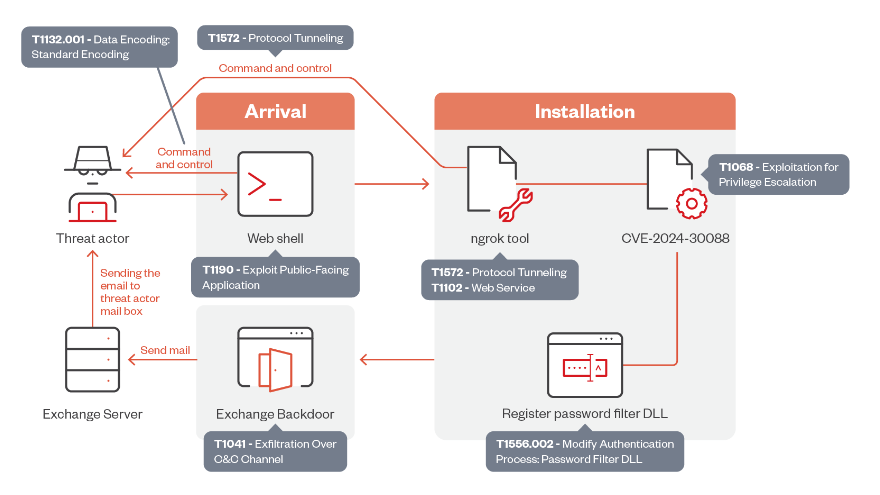
First, a vulnerable web server is compromised to release a web shell. Next, the ngrok remote management tool is released to continue the attack and spread to more network endpoints. The backdoor, codenamed STEALHOOK, which is in charge of sending harvested data via the Exchange server to an email account under the attacker's control in the form of attachments, is then delivered through the privilege escalation vulnerability.
Using elevated capabilities to drop the password filter policy DLL (psgfilter.dll) to obtain sensitive credentials from domain users via domain controllers or local accounts on local workstations is a noteworthy method utilized by OilRig in their most recent round of attacks. The threat actor implemented the password filter export functions with extreme caution, dealing with unencrypted passwords. Additionally, the threat actor used plaintext passwords to obtain access and remotely launch tools. The credentials in plaintext were first encrypted and then transferred over networks to be exfiltrated.
It's important to remember that psgfilter.dll was used in December 2022 in conjunction with a campaign that used MrPerfectionManager, another backdoor, to target Middle Eastern businesses. Based on their previous actions, it appears that OilRig is concentrating on exploiting flaws in vital infrastructure located in politically vulnerable areas. To use these as weapons to strike other targets, they also try to gain a stable foothold in compromised institutions.
Impact
- Privilege Escalation
- Credential Theft
- Data Exfiltration
- Unauthorized Access
- Cyber Espionage
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- 5b974268236aafd6dc7151758e508069
- 73690743aea09a345dbdfe828f069370
- ee59031802287179d0abaac41fb34a66
- 60adbb2a2aa829c0ef7bbfce5214ff82
- db89ec570e6281934a5c5fcf7f4c8967
SHA-256
- a24303234e0cc6f403fca8943e7170c90b69976015b6a84d64a9667810023ed7
- b3257f0c0ef298363f89c7a61ab27a706e9e308c22f1820dc4f02dfa0f68d897
- 54e8fbae0aa7a279aaedb6d8eec0f95971397fea7fcee6c143772c8ee6e6b498
- 98fb12a9625d600535df342551d30b27ed216fed14d9c6f63e8bf677cb730301
- edfae1a69522f87b12c6dac3225d930e4848832e3c551ee1e7d31736bf4525ef
SHA-1
- da46c32cb849b908eef609b5aa64ec5d5495f032
- 0db1dc66c2813c4db5a8b533f420d4330c4c9f77
- d6d8a9fa40bc691eb42f0faaebcdea4ef27ee0dc
- d3a23b8c9e125cfc6bae2d6006ff406f3c02c4cd
- 0098c79e1404b4399bf0e686d88dbf052269a302
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Refer to Microsoft Security Advisory for patch, upgrade, or suggested workaround information.
- Ensure all operating systems and software are up to date with the latest security patches.
- Employ reliable antivirus and antimalware software to detect and block known threats.
- Regularly update these tools to maintain the latest threat intelligence.
- Implement IDPS to detect and prevent unusual network activity, system behavior, or similar threats.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your accounts adds an extra layer of security and can help prevent unauthorized access even if your login credentials have been stolen.
- Regularly backing up your important data can help ensure that you don’t lose any critical information in the event of a malware infection or other data loss event.
- Be wary of emails, attachments, and links from unknown sources. Also, avoid downloading software from untrusted sources or clicking on suspicious ads or pop-ups.
- Use email filtering solutions to block malicious attachments and links that may deliver malware to users via phishing emails.
- Segment your network to limit lateral movement for attackers.
- Employ application whitelisting to only allow approved software to run on systems, reducing the risk of unauthorized applications being executed.
- Implement robust monitoring solutions to detect any unusual or suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration. Establish an effective incident response plan to respond to and mitigate any potential breaches quickly.
- Make sure all of your software, including your operating system and applications, is up-to-date with the latest security patches. This can help prevent vulnerabilities that info-stealers and other types of malware could exploit.

