Severity
High
Analysis Summary
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered an ongoing phishing campaign named REF6127 that uses job-themed lures to deliver a Windows-based backdoor called WARMCOOKIE. This backdoor is used for initial reconnaissance and deploying additional payloads.
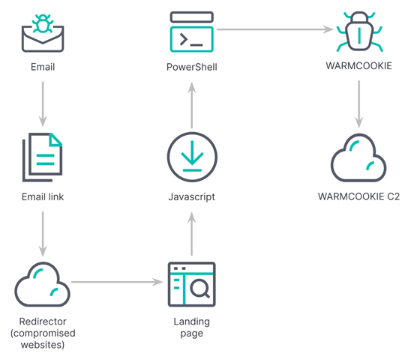
Each sample of WARMCOOKIE includes a hard-coded command-and-control IP address and an RC4 key for encryption. The malware is capable of fingerprinting infected machines, capturing screenshots, and deploying more malicious programs. Since late April, attack chains have involved emails from fake recruitment firms urging recipients to view job details by clicking a link which leads to a CAPTCHA challenge and the download of a malicious JavaScript file.
Researchers said in a new analysis that a JavaScript file named "Update_23_04_2024_5689382.js" runs an obfuscated script that executes PowerShell commands to load WARMCOOKIE. This script exploits the Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) to download the backdoor. The campaign uses compromised infrastructure to host the initial phishing URLs which redirect victims to a landing page where the infection process begins. WARMCOOKIE establishes persistence on infected machines through a scheduled task and performs anti-analysis checks to evade detection before launching its core functions. These functions include reading and writing files, executing commands, fetching installed applications, and taking screenshots.
WARMCOOKIE shares similarities with malware from a previous campaign called Resident which targeted sectors like manufacturing, commercial, and healthcare. Researchers noted that WARMCOOKIE is gaining popularity for its straightforward functionality which allows threat actors to monitor victims and deploy more harmful payloads such as ransomware.
Experts have also detailed another phishing campaign using invoice-related decoys and the Windows search functionality embedded in HTML to deploy malware. This campaign employs ZIP archives containing HTML files that leverage the "search:" URI protocol handler to trick users into executing malicious scripts. These sophisticated phishing techniques exploit users' trust in familiar interfaces and actions such as clicking email attachments.
Impact
- Cyber Espionage
- Command Execution
- File Encryption
- Exposure of Sensitive Data
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- omeindia.com
- assets.work-for.top
IP
- 45.9.74.135
- 80.66.88.146
- 185.49.69.41
MD5
- 1b7b6fb1a99996587a3c20ee9c390a9c
SHA-256
- ccde1ded028948f5cd3277d2d4af6b22fa33f53abde84ea2aa01f1872fad1d13
SHA1
- 129aa22329dd45f7bce5172e97cbd8016dec830e
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.
- Implement multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security to login processes.
- Regularly monitor network activity for any unusual behaviour, as this may indicate that a cyberattack is underway.
- Organizations need to stay vigilant and follow best practices for cybersecurity to protect their systems and data from potential threats. This includes regularly updating software and implementing strong access controls and monitoring tools.
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to respond effectively in case of a security breach or data leakage.
- Maintain regular backups of critical data and systems to ensure data recovery in case of a security incident.
- Adhere to security best practices, including the principle of least privilege, and ensure that users and applications have only the necessary permissions.
- Establish a robust patch management process to ensure that security patches are evaluated, tested, and applied promptly.
- Conduct security audits and assessments to evaluate the overall security posture of your systems and networks.
- Implement network segmentation to contain and isolate potential threats to limit their impact on critical systems.

