Severity
High
Analysis Summary
In May 2024, a phishing attack targeting an unnamed industrial services company was thwarted. More_eggs, a modular backdoor used to harvest sensitive information, is operated by the Golden Chickens threat group and offered as Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) to other criminal entities.
This technique, originally detected over two years ago, highlights the ongoing use of social engineering to trick professionals, particularly on LinkedIn, into downloading the malware. According to the researchers, the attack involved distributing the More_eggs malware disguised as a resume aimed at a recruiter who was deceived into visiting a fake resume download site. The attack chain involved the malicious actors responding to LinkedIn job postings with a link to a fake resume download site which led to the download of a malicious Windows Shortcut file (LNK).
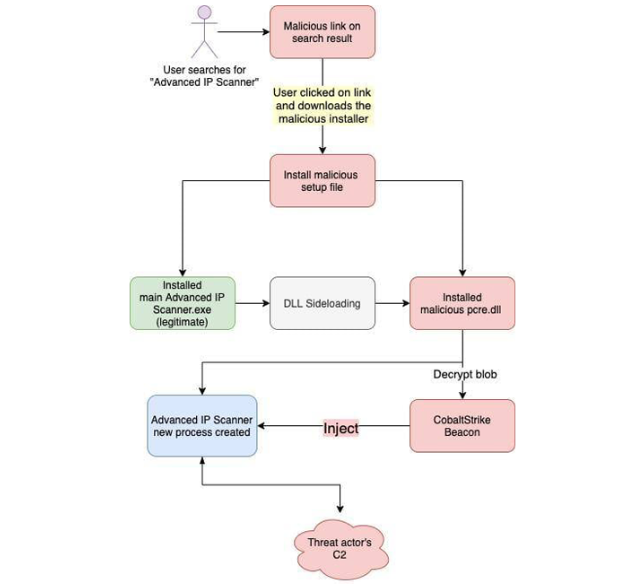
This LNK file then retrieved a malicious DLL via a legitimate Microsoft program, ie4uinit.exe, and executed it using regsvr32.exe. This sequence allowed the malware to establish persistence, gather data from the infected host, and deploy additional payloads including the JavaScript-based More_eggs backdoor. Notably, the URL used for the initial attack later displayed a legitimate-looking resume obscuring the malicious activity.
In addition, the More_eggs campaign disclosed a drive-by download campaign involving fake websites distributing Vidar Stealer through the KMSPico Windows activator tool. These fake sites hosted behind Cloudflare Turnstile required human interaction to download a ZIP package making it difficult for automated web crawlers to detect. Similarly, security researchers reported on social engineering campaigns that set up lookalike sites to distribute Cobalt Strike, further showcasing the varied tactics cybercriminals employ.
Another significant threat highlighted is the emergence of the V3B phishing kit which targets banking customers in the European Union. Active since March 2023 and sold via a Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) model, V3B offers customized templates for over 54 banks in the region, enabling real-time interaction with victims to steal credentials and one-time passwords. The kit supports sophisticated attacks such as QR code login jacking for services like WhatsApp. Experts noted that hundreds of cybercriminals are using this kit to defraud victims, leaving many with drained bank accounts.
Impact
- Sensitive Information Theft
- Credential Theft
- Financial Loss
Indicators of Compromise
URL
- http://a8advbiejf.christianvelour.com/sfglfjgg4ks4f
- https://dcc.olcrv.com/login/tologin
- http://2944839123.christianvelour.com/33/ff5427fd446c109da7ef5ed0667c0025/2138989162
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.
- Implement multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security to login processes.
- Regularly monitor network activity for any unusual behavior, as this may indicate that a cyberattack is underway.
- Organizations need to stay vigilant and follow best practices for cybersecurity to protect their systems and data from potential threats. This includes regularly updating software and implementing strong access controls and monitoring tools.
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to respond effectively in case of a security breach or data leakage.
- Maintain regular backups of critical data and systems to ensure data recovery in case of a security incident.
- Adhere to security best practices, including the principle of least privilege, and ensure that users and applications have only the necessary permissions.
- Establish a robust patch management process to ensure that security patches are evaluated, tested, and applied promptly.
- Conduct security audits and assessments to evaluate the overall security posture of your systems and networks.
- Implement network segmentation to contain and isolate potential threats to limit their impact on critical systems.

