Severity
High
Analysis Summary
A new attack has been found by cybersecurity experts that targets cloud-hosted large language model (LLM) services using credentials that have been taken from the cloud to sell access to other threat actors. The attack method is named as LLMjacking.
After gaining initial access, they tried to access local LLM models hosted by cloud providers by exfiltrating cloud credentials and entering the cloud environment. This time, Anthropic's local Claude (v2/v3) LLM model was the focus. The method by which the attack chain was carried out involves breaking into a system that is using a vulnerable version of the Laravel Framework (such as CVE-2021-3129), and then obtaining credentials from Amazon Web Services (AWS) to gain access to the LLM services.
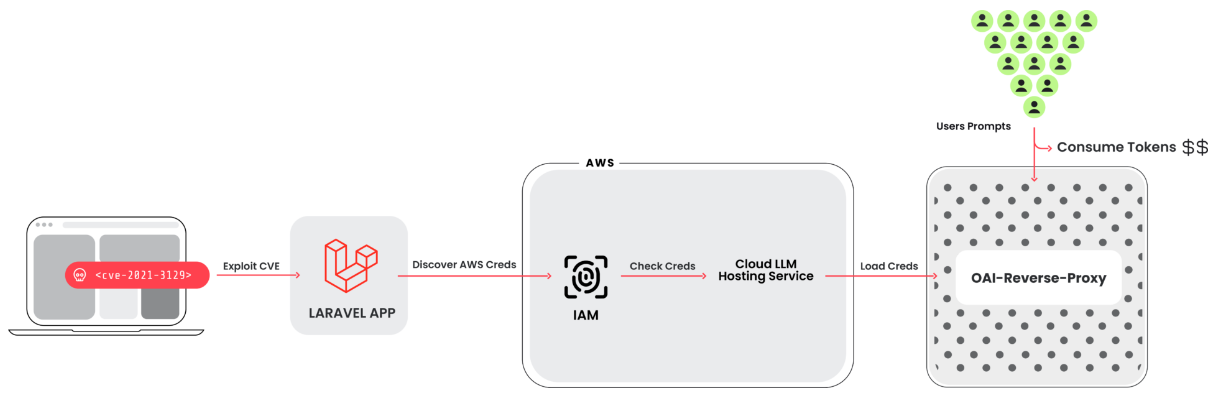
An open-source Python script that verifies and examines keys for a variety of services from Anthropic, AWS Bedrock, Google Cloud Vertex AI, Mistral, and OpenAI, among others, is one of the tools utilized. The researchers noticed that during the verification stage, no real LLM queries were executed. Rather, only enough was done to determine any quotas and what the credentials were capable of. The fact that the key checker is integrated with oai-reverse-proxy, an additional open-source application that serves as a reverse proxy server for LLM APIs, suggests that the threat actors are probably granting access to the compromised accounts without really disclosing the underlying credentials.
A reverse proxy like this may help the attackers make money from their efforts if they were compiling a list of relevant credentials and wanted to charge for access to the accessible LLM models. Additionally, it appears that the attackers are trying to evade detection by querying the logging settings when they run their prompts using the compromised credentials.
Attackers can now monetarily monetize their access to the LLMs while the cloud account owner pays the bill without their knowledge or agreement, marking a change from attacks that concentrate on prompt injections and model poisoning. This type of attack might cost the victim more than $46,000 in LLM consumption every day.
Depending on the model and how many tokens are fed into it, using LLM services can be costly. Attackers can potentially prevent the compromised firm from employing models lawfully by maximizing the quota limits, which would interfere with regular commercial activities. To prevent initial access, it is advised that organizations enable extensive logging, keep an eye out for any suspicious or illegal activity in cloud logs, and make sure that efficient vulnerability management procedures are in place.
Impact
- Credential Theft
- Unauthorized Access
Indicators of Compromise
IP
- 83.7.139.184
- 83.7.157.76
- 73.105.135.228
- 83.7.135.97
Remediation
- Ensure that general security policies are employed including implementing strong passwords, correct configurations, and proper administration security policies.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions promptly. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets.
- Deploy advanced threat detection solutions that can identify and analyze suspicious activities, patterns, and behaviors across your network and endpoints. Utilize intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and next-generation firewalls to proactively monitor and block malicious activities.
- Implement network segmentation to compartmentalize sensitive systems and data.
- Strengthen email security protocols to identify and block phishing attempts. Train employees to recognize suspicious emails and attachments, and employ email filtering technologies to reduce the likelihood of successful spear-phishing attacks.
- Regularly update and patch all software, applications, and operating systems to minimize potential entry points for cyber attackers.
- Enforce MFA across your organization to add an extra layer of security to user accounts and critical systems.
- Deploy advanced endpoint security solutions that offer real-time threat detection and response. This includes antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, and behavioral analysis to identify suspicious activities.
- Ensure that systems are securely configured and hardened following industry best practices. Disable unnecessary services, ports, and protocols to reduce the attack surface.
- Develop and regularly update an incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a cyber attack. This plan should include communication protocols, roles and responsibilities, and procedures for containing and mitigating the attack.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your systems and infrastructure.

