Severity
High
Analysis Summary
As part of a social engineering attempt, a threat actor group associated with Iran's Revolutionary Guard Corps' intelligence branch impersonated journalists and human rights advocates. According to cybersecurity analysts, the campaign was executed by APT42.
The Washington Post, The Economist, and The Jerusalem Post are among the news outlets that were impersonated in the operation. According to the researchers, prominent Washington think tanks like the McCain Institute, the Aspen Institute, and the Washington Institute were all spoofed by the group.
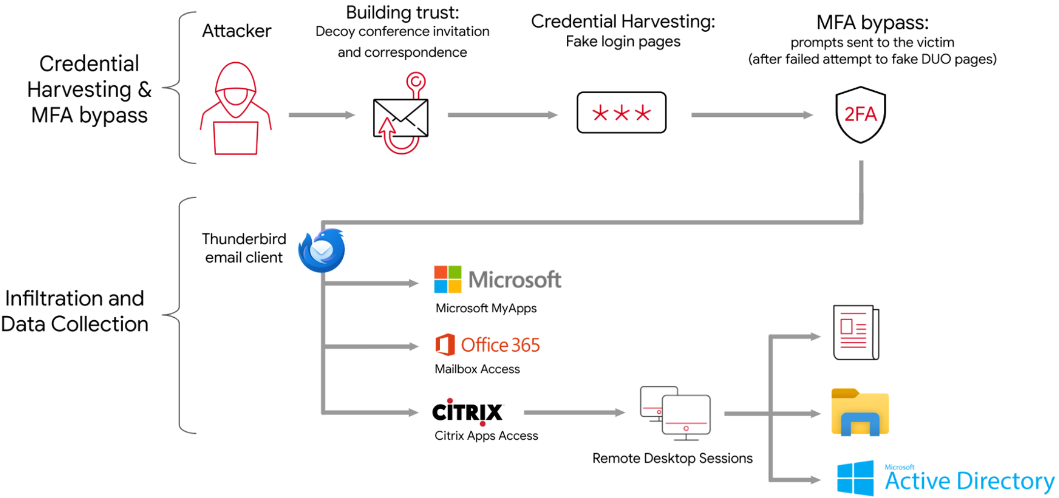
The Iranian threat actors sent phishing lures to targets to harvest their credentials by impersonating these companies. In other instances, the attackers pretended to be in charge of file hosting companies, generic login pages, and reputable websites like YouTube, Gmail, Google Meet, and Google Drive. APT42 has been seen pretending to be journalists and event planners to establish credibility with victims through consistent communication and to send invitations to conferences or authentic documents. APT42 was able to obtain credentials through these social engineering techniques and utilize them to obtain initial access to Cloud environments.
There isn't any proof that the spoofed companies were in any way compromised or breached. This report is the most recent in a long line of instances when Iranian hacker outfits have deceived their victims by using false identities. Cybersecurity specialists revealed last year that APT42 was attempting to exploit these personas and social media accounts to carry out phishing attempts against Iranian-focused researchers worldwide, including requesting them to participate in an upcoming Atlantic Council report.
Researchers say that since at least 2019, members of APT42—also known by the aliases Charming Kitten, TA453, Mint Sandstorm, and Mint Phosphorous—have been involved in a broad social engineering campaign. The ultimate objective of the endeavor seems to be espionage since the threat group uses the credentials it has taken to get access to the Cloud environments of its victims and steal information that Tehran finds strategically valuable.
One incident occurred in February when the gang operated a domain that housed a document purportedly advocating women's rights on DropBox. To add credibility to the trap, the domain assumed the identities of an Iranian director and a Fox News commentator. In an apparent attempt to capitalize on interest in the ongoing Israel-Gaza war, a fictitious document titled "The Secrets of Gaza Tunnels" was hosted on another domain in March.
The fact that the documents themselves were frequently free of malware suggests that the attackers were attempting to build trust with the target businesses and create the framework for credential phishing. After gaining credentials, the actors used cloned websites to collect MFA tokens and sent push alerts to victims to get around multifactor authentication security. Due to the easier access to the victims' Microsoft 365 cloud environments, APT42 was able to obtain documents about Iranian geopolitical interests as well as data from OneDrive and Outlook emails. The perpetrator concealed their presence in victim networks by utilizing a combination of open-source tools and built-in characteristics.
The techniques used by APT42 leave no trace of their operations, which may make it harder for network defenders to identify and stop them. Since the beginning of the Israel-Gaza conflict, other Iranian threat groups have shifted their attention to disruptive and destructive attacks, while APT42 has stayed steadfastly committed to its custom of gathering intelligence from foreign targets.
Impact
- Identity Theft
- Credential Theft
- Unauthorized Access
- Cyber Espionage
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- acconut-signin.com
- account-signin.com
- accredit-validity.online
- activity-permission.online
- admin-stable-right.top
- admiscion.online
- avid-striking-eagerness.online
- bitly.org.il
- check-panel-status.live
MD5
- 347b273df245f5e1fcbef32f5b836f1d
- d7bf138d1aa2b70d6204a2f3c3bc72a7
- c23663ebdfbc340457201dbec7469386
- d5a05212f5931d50bb024567a2873642
SHA-256
- 0e51029ba28243b0a6a071713c17357a8eb024aa4298d1ccc9e2c4ac8916df4d
- 5404e39f2f175a0fc993513ee52be3679a64c69c79e32caa656fbb7645965422
- dbdb14e37fc4412711a1e5e37e609e33410de31de13911aee99ab473753baa4a
- e0ba0cedd8a8624c75af29965e5fa7ab754fc0fcddbb330bb548dab4f2be333f
SHA1
- 986b68167fb0fc3ffb3985451d431c861afaeba4
- 3fd06c930ddc4b1914151f69454c087a42413a24
- 97e48fbb46f52d5a35360f9bfd8a2877a4a7fe70
- 70065b263f14c48eeb86e2436ba064c531670e71
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls
- Disseminate information regarding the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by the APT42 group to target dissidents.
- Educate potential targets on the risks associated with engaging in online conversations with unknown individuals, especially on social media platforms.
- Encourage individuals to use secure communication tools and platforms that offer end-to-end encryption to protect sensitive information.
- Conduct phishing awareness training to help them recognize and avoid social engineering attacks, such as deceptive messages and links.
- Advise users to enable MFA on their accounts to add an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Ensure that all devices and software used are up to date with the latest security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Train individuals to be cautious when interacting with unknown individuals online and to be vigilant about unusual or suspicious requests.
- Implement network monitoring and intrusion detection systems to detect any unauthorized access attempts or unusual activities.
- Recommend the use of secure messaging and communication platforms that offer end-to-end encryption and protect conversations from interception.

