Severity
High
Analysis Summary
The STOP/DJVU ransomware initially made headlines in 2018 and has since been attacking individuals all around the world. It’s widespread on torrent sites and other platforms in software crack packages and adware bundles. DJVU Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts files on an infected computer and demands a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. The STOP/DJVU Ransomware family is one of the most prevalent ransomware threats and is known for its aggressive tactics and high-pressure ransom demands.
Malware is delivered via cracked applications, fake set-up app keygens, activators, and Windows updates. It does not utilize local information like keyboard layouts or timezone settings to prevent infecting victims in certain countries; instead, it uses the information returned by a request. The card’s MAC address is utilized to provide unique identification for the system. This identity is provided to STOP’s command and control server, which responds with an RSA-2048 public key for encryption. Additional malware, including an information stealer known as Vidar, is then downloaded and installed.
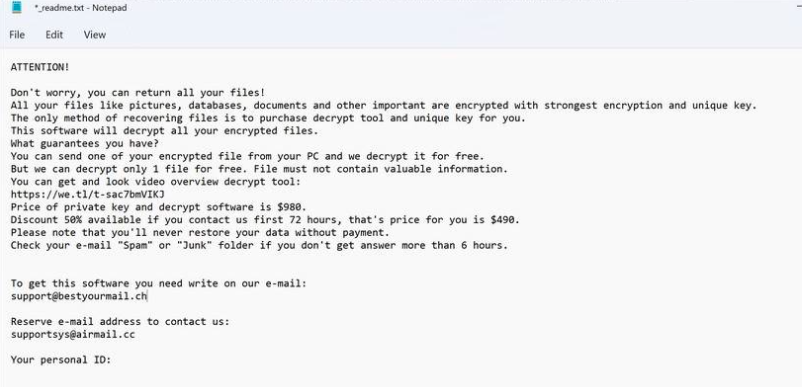
Ransom note:
Impact
- Information Theft
- File Encryption
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- 5093f66a39d5e25aa3eec6a1181a03b8
- bd4d06f1e0139f61fed18f524e00ff59
SHA-256
- 2545f1ee454e96b5c1d06c7a675488615ff98cd1baca629963172b466e57fd31
- c4b93b302d810c73be3886dc8aa03c230adb8a5df3611bedfa92995412fe2781
SHA1
- b5eff256d3f1639515ea8e6bbd568eedba571690
- 8a8cf66f6ecd4b4591ab7839e7865c55d287e760
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Maintain Offline Backups - In a ransomware attack, the adversary will often delete or encrypt backups if they have access to them. That’s why it’s important to keep offline (preferably off-site), encrypted backups of data and test them regularly.
- Emails from unknown senders should always be treated with caution.
- Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.

