Severity
High
Analysis Summary
North Korea’s infamous advanced persistent threat (APT) group known as Lazarus is now linked to a newly emerging global campaign that leverages the exploitation of vulnerabilities present in Log4j to distribute previously unknown remote access trojans (RATs) on target devices.
The activity cluster is being tracked by researchers under the name ‘Operation Blacksmith’, in which they have observed the use of three Dlang-based malware families that include a RAT dubbed NineRAT, DLRAT, and a downloader called BottomLoader. NineRAT utilizes Telegram for performing command-and-control (C2) communication.
The researchers describe the tactics used in the latest campaign as a defining shift and having an overlap with the sub-group cluster of Lazarus called Andariel (aka Silent Chollima and Onyx Sleet). It is noticeable from previous campaigns that Andariel is usually tasked with gaining initial access, performing reconnaissance, and maintaining persistence for espionage activities to support the North Korean government’s interests.
The campaign mainly targets the manufacturing, physical security, and agricultural sectors. It is a fact that 2.8% of applications still use vulnerable versions of the Log4Shell library even after two years of public disclosure, and another 3.8% using Log4j 2.17.0, which doesn’t make it surprising that Lazarus has chosen to exploit these vulnerabilities.
“This campaign consists of continued opportunistic targeting of enterprises globally that publicly host and expose their vulnerable infrastructure to n-day vulnerability exploitation such as CVE-2021-44228 (Log4j),” said the security researchers.
NineRAT was developed around May 2022 and was first used in March 2023 in a cyberattack that targeted a South American agricultural organization. Later in September 2023, it was used again to attack a European manufacturing company using a legitimate messaging service like Telegram for C2 communications.
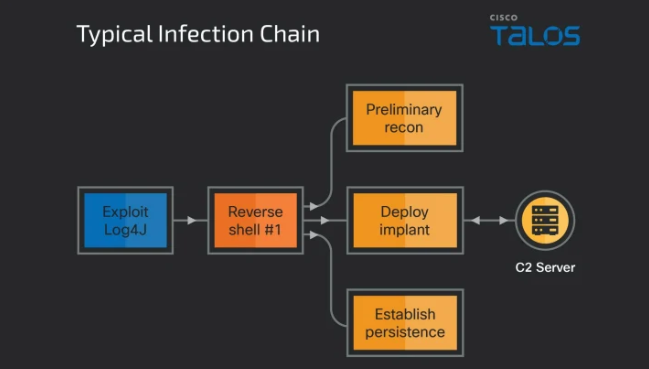
The malware allows the threat actors to send commands and gather system information, download additional payloads, upload files, and uninstall or update itself. When NineRAT is launched, it receives preliminary commands from its Telegram C2 channel to re-fingerprint the compromised systems. This indicates that the data collected by Lazarus using NineRAT is probably shared with other APT groups.
After the initial reconnaissance, another tool used in the attacks is a custom proxy malware called HazyLoad, previously identified by Microsoft’s analysis team to be used by the threat group as part of intrusions to weaponize critical vulnerabilities in JetBrains TeamCity (CVE-2023-42793). A downloader malware called BottomLoader is used to install and execute HazyLoad.
Another RAT that Operation Blacksmith has been spreading is DLRAT, which is a downloader and RAT combined in one which is used to carry out system reconnaissance, receive commands from the C2 to execute them, and deploy additional payloads in the infected devices. Lazarus’s use of various tools makes it challenging to analyze and detect, resulting in highly persistent access.
Andriel has exploited Log4Shell previously as an initial access vector for deploying a remote access trojan called EarlyRAT. The disclosure comes as researchers detailed the use of Autolt versions of malware like Amadey and RftRAT by the Kimsuky APT group and spread them using spear-phishing emails containing malicious attachments and links. Kimsuky operates under North Korea’s Reconnaissance General Bureau (RGB), which is also responsible for funding the Lazarus group.
Impact
- Cyber Espionage
- Sensitive Information Theft
- Code Execution
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- 19a05a559b0c478f3049cd414300a340
- 96d98c83daf368066efe3dd41a0dc622
- 490bb2abfdd5d4e185325c3a9fb9f5d7
- 12e399411185e386c863954eaa6f6595
- d13ac94aec9d82523b27d3c659e38d8a
- ea853503ca1681e07de3e556604c4af7
- d9731b51c936aa57207b0efe435ab056
- f8f7eced1411d76e2a0319151ecf80b7
- 9846e2e45000984719804ec2236405bd
- d62126246776ddf0ad64df8c78552805
SHA-256
- 000752074544950ae9020a35ccd77de277f1cd5026b4b9559279dc3b86965eee
- 534f5612954db99c86baa67ef51a3ad88bc21735bce7bb591afa8a4317c35433
- ba8cd92cc059232203bcadee260ddbae273fc4c89b18424974955607476982c4
- 47e017b40d418374c0889e4d22aa48633b1d41b16b61b1f2897a39112a435d30
- f91188d23b14526676706a5c9ead05c1a91ea0b9d6ac902623bc565e1c200a59
- 5b02fc3cfb5d74c09cab724b5b54c53a7c07e5766bffe5b1adf782c9e86a8541
- 82d4a0fef550af4f01a07041c16d851f262d859a3352475c62630e2c16a21def
- 0e416e3cc1673d8fc3e7b2469e491c005152b9328515ea9bbd7cf96f1d23a99f
- e615ea30dd37644526060689544c1a1d263b6bb77fe3084aa7883669c1fde12f
- 9a48357c06758217b3a99cdf4ab83263c04bdea98c347dd14b254cab6c81b13a
SHA-1
- fadbbb63e948b5b3bbbaeedc77e69472143a3b86
- be49443603068d9913b4634126749217df6a695e
- 4bf18f50f8496813e424c7c8dc7aab68cee86afd
- 8cf133d72ba6d476e28dfc18e3ba13dc15f99071
- 24afe860baf3379a77527c561030bce78ee1e614
- 9677ecca60f76d8e2a3adec939f48d14e32f91b9
- 9e223444d7b6b1837c4643f34e0f561613496569
- 3c5f4caf1a9d08d939a7d31f5ddb232806746b56
- f1b325a6b927f62a911dd3bf199262223983fbb9
- 9285f2d790c65c94e382463bfff17a642b2b9762
Domain Name
- tech.micrsofts.com
- tech.micrsofts.tech
URL
- http://27.102.113.93/inet.txt
- http://162.19.71.175:7443/sonic/bottom.gif
- http://201.77.179.66:8082/img/lndex.php
- http://201.77.179.66:8082/img/images/header/B691646991EBAEEC.gif
- http://201.77.179.66:8082/img/images/header/7AEBC320998FD5E5.gif
Remediation
- Upgrade to the latest version of Log4j, available from the Apache Website.
- Always be suspicious about emails sent by unknown senders.
- Never click on links/attachments sent by unknown senders.
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise IOCs in your environment utilizing your respective security controls.
- Ensure that general security policies are employed including: implementing strong passwords, correct configurations, and proper administration security policies
- Enable two-factor authentication.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions promptly. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets.

