Severity
High
Analysis Summary
A new Android malware campaign that is mainly targeting Iranian banks has added sophisticated evasion tactics into its arsenal to avoid being detected. Researchers have discovered over 200 malicious apps that are associated with this operation and the threat actor also carried out phishing attacks against financial institutions.
The campaign was first discovered in late July 2023 when researchers revealed information about a cluster of 40 apps used for harvesting credentials targeting the users of some of the biggest Iranian banks. The main goal of these fake apps is to trick the victims into giving them extensive permissions and exfiltrate banking login credentials and credit card details by exploiting Android’s accessibility services.
There are a large number of newly registered domains that offer downloads of these malicious fake apps, some of these domains also being used as command-and-control (C2) servers by the threat actors. A few of the domains are also observed to show HTML phishing pages that are made to steal credentials from mobile users.
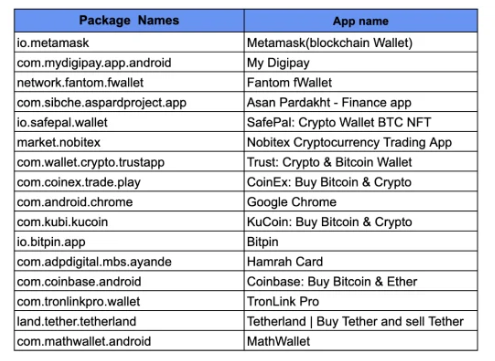
The latest discoveries show that the threat has continued evolving in the last six months in terms of a wider set of targeted banks and cryptocurrency wallet apps, as well as bringing in previously undocumented features. These include using accessibility services for additional permissions and preventing uninstallation.
Some variants of the malware are also capable of accessing a README file present in GitHub repositories to fetch a Base64-encoded version of the C2 server and phishing URLs, allowing the threat actors to quickly respond when phishing sites are taken down by updating the repository to make sure the malicious apps can easily access the latest phishing site.
There is some evidence showing that Apple’s iOS operating system is also a potential target for the campaign since the phishing websites verify if the page is opened by an iOS device. If it is, then the unsuspecting user is redirected to a website that pretends to be an iOS version of the banking app.
The phishing campaigns are also highly sophisticated as they impersonate real websites for exfiltrating credentials, device models, account numbers, and IP addresses and deliver the information to the two actor-controlled Telegram channels.
The researchers concluded, “It is evident that modern malware is becoming more sophisticated, and targets are expanding, so runtime visibility and protection are crucial for mobile applications.”
Impact
- Sensitive Data Theft
- Financial Loss
- Credential Theft
Indicators of Compromise
Domain Name
- rm-melat-4.com
- app1mel.click
- hmrahbink.click
- mellatapp2.click
- mappnew1.shop
- sbam1.site
URL
- http://bameman.click/webview
- http://saderate-be.shop/
- http://giftemali.click/webview
- http://rat-tejrat1.shop/webview
- http://1inch.today/
- http://bc-games-login.info/webview
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls
- Emails from unknown senders should always be treated with caution.
- Patch and upgrade any platforms and software timely and make it into a standard security policy. Prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities and zero-days.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions promptly. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets.
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Conduct thorough code reviews and dependency analysis to identify and scrutinize all third-party dependencies, including open-source packages. Regularly update and patch these dependencies to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
- Never download apps from suspicious websites and always check the validity of the vendor.
- Enable MFA for banking and sensitive applications to add an extra layer of security.
- Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in both systems and user practices.

